DARPA has achieved a significant breakthrough in wireless power transmission, successfully beaming energy over five miles and using it to pop popcorn, marking a major step towards practical, long-range wireless power applications.
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) recently demonstrated its Focused Research Initiative for Wireless Power (FRiW) program’s capabilities by wirelessly transmitting substantial power over a distance of five miles. This feat, highlighted by the successful popping of popcorn using the wirelessly transmitted energy, represents a pivotal moment in the pursuit of ubiquitous wireless power, according to program managers. The successful test has demonstrated the potential for future military applications and potential civilian applications, such as remote charging of drones and powering remote sensors.
The FRiW program, aimed at revolutionizing how power is delivered and utilized, has been exploring various innovative approaches to wireless power transmission. Central to this initiative is overcoming the challenges associated with long-range power transfer, which traditionally suffers from significant energy loss and dispersion. DARPA’s recent experiment showcases the effectiveness of its technologies in mitigating these issues, paving the way for more efficient and reliable wireless power systems.
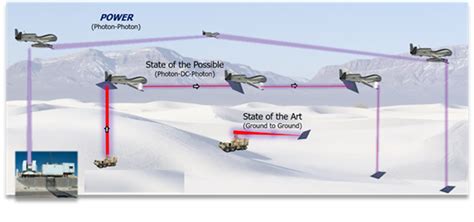
The experiment, conducted at a test range, involved a ground-based transmitter beaming radiofrequency (RF) energy towards a receiver located five miles away. The receiver was connected to a popcorn machine, which successfully popped kernels using the wirelessly transmitted power. This demonstration was not merely a novelty; it served as a tangible illustration of the technology’s potential to deliver usable energy over considerable distances.
According to Paul Jaffe, an aerospace engineer, such demonstrations “show that you can actually deliver meaningful amounts of power to a remote location for practical purposes,”. The key innovation lies in the advanced beamforming and power management techniques employed by DARPA, which minimize energy loss and ensure a focused and stable power delivery.
The implications of this breakthrough are far-reaching, potentially transforming various sectors, including defense, logistics, and energy distribution. For the military, wireless power could enable the remote charging of drones, powering of forward operating bases, and the elimination of the logistical challenges associated with transporting fuel and batteries. In the civilian realm, wireless power could revolutionize energy distribution, providing a means to power remote areas, charge electric vehicles wirelessly, and create more sustainable and resilient energy systems.
Technical Details and Innovations
DARPA’s FRiW program has focused on several critical technological areas to achieve its wireless power transmission goals. These include:
- Beamforming: This technique involves precisely directing the RF energy towards the receiver, minimizing dispersion and maximizing the amount of power received. Advanced beamforming algorithms and antenna designs are crucial for achieving high efficiency and accuracy.
- Power Amplification: Efficient power amplifiers are essential for converting electrical energy into RF energy with minimal loss. DARPA has been exploring novel amplifier designs and materials to improve efficiency and reduce heat dissipation.
- Receiver Design: The receiver must be capable of efficiently capturing the RF energy and converting it back into electrical energy. Advanced rectenna (rectifying antenna) designs and energy harvesting techniques are critical for maximizing the amount of usable power.
- Atmospheric Compensation: The atmosphere can significantly affect the propagation of RF energy, causing signal attenuation and distortion. DARPA has been developing techniques to compensate for these atmospheric effects, ensuring a stable and reliable power link.
- Safety Mechanisms: Ensuring the safety of wireless power transmission is paramount. DARPA has implemented various safety mechanisms to prevent overexposure to RF energy and mitigate potential risks.
The successful popcorn-popping demonstration highlights the effectiveness of these technologies in delivering meaningful amounts of power over long distances. The experiment involved a carefully calibrated setup, with detailed measurements taken to assess the efficiency and stability of the power link. The data collected from the experiment will be used to further refine the technology and improve its performance.
Potential Military Applications
The military applications of wireless power are particularly compelling, offering the potential to revolutionize battlefield logistics and operational capabilities. Some key potential applications include:
- Remote Drone Charging: Drones are increasingly used for surveillance, reconnaissance, and even combat missions. Wireless power could enable drones to be recharged remotely, extending their flight time and operational range without the need for physical charging stations.
- Forward Operating Base (FOB) Power: Supplying FOBs with fuel and batteries is a significant logistical challenge. Wireless power could provide a means to power FOBs remotely, reducing the need for convoys and minimizing the risk of attacks.
- Remote Sensor Power: Military operations often rely on remote sensors to monitor enemy activity and gather intelligence. Wireless power could enable these sensors to operate for extended periods without the need for battery replacements, enhancing their effectiveness and reducing maintenance costs.
- Directed Energy Weapons: While further in the future, the technology to accurately transfer power over long distances has implications in the directed energy weapons sector. Supplying energy directly to defensive weapons systems could reduce energy storage needs and enable increased readiness and operational time.
DARPA is actively exploring these potential military applications, conducting field tests and simulations to assess the feasibility and effectiveness of wireless power in various operational scenarios. The agency is also working closely with the military services to identify specific needs and develop tailored solutions.
Civilian Applications and Future Prospects
Beyond military applications, wireless power holds immense potential for transforming various civilian sectors, offering the promise of more sustainable, efficient, and convenient energy solutions. Some key potential applications include:
- Remote Power for Rural Areas: Many rural areas lack access to reliable electricity. Wireless power could provide a means to deliver electricity to these areas, improving quality of life and enabling economic development.
- Wireless Charging of Electric Vehicles: Wireless charging could revolutionize the electric vehicle industry, making it more convenient and practical to own and operate electric vehicles. Imagine being able to charge your car simply by parking it in your garage or at a charging pad, without the need for cables or plugs.
- Industrial Automation: Wireless power could enable more flexible and efficient industrial automation systems. Robots and other automated equipment could be powered wirelessly, eliminating the need for cables and allowing for greater mobility and flexibility.
- Disaster Relief: In the aftermath of natural disasters, power grids are often disrupted. Wireless power could provide a means to quickly restore power to affected areas, facilitating rescue efforts and providing essential services.
- Wireless Sensor Networks: Wireless power could enable the deployment of large-scale wireless sensor networks for environmental monitoring, infrastructure management, and other applications. These sensors could be powered wirelessly, eliminating the need for batteries and reducing maintenance costs.
- Consumer Electronics: While further in the future with current long-range technology, smaller scale applications can lead to wireless charging of consumer electronics, such as smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices.
The development of wireless power technology is still in its early stages, but the recent progress made by DARPA and other researchers is encouraging. As the technology matures, it has the potential to revolutionize how we generate, distribute, and use energy, creating a more sustainable and convenient future.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the immense potential of wireless power, there are still several challenges and considerations that must be addressed before it can be widely adopted. These include:
- Efficiency: Improving the efficiency of wireless power transmission is crucial for making it economically viable. Current wireless power systems still suffer from significant energy loss, particularly over long distances.
- Safety: Ensuring the safety of wireless power transmission is paramount. Exposure to high levels of RF energy can be harmful, and it is essential to develop safety standards and regulations to protect the public.
- Cost: The cost of wireless power systems is currently high, which limits their widespread adoption. As the technology matures and production volumes increase, the cost is expected to decrease.
- Regulations: Clear regulatory frameworks are needed to govern the use of wireless power technology. These frameworks should address issues such as spectrum allocation, safety standards, and environmental concerns.
- Environmental Impact: The environmental impact of wireless power transmission needs to be carefully considered. The use of RF energy can potentially interfere with wildlife and ecosystems, and it is important to minimize these impacts.
Addressing these challenges and considerations is essential for realizing the full potential of wireless power and ensuring that it is deployed responsibly and sustainably.
The Future of Wireless Power
The future of wireless power is bright, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. As the technology matures, it is expected to play an increasingly important role in various sectors, transforming how we generate, distribute, and use energy.
DARPA’s FRiW program is at the forefront of this revolution, pushing the boundaries of what is possible and paving the way for a future where power can be delivered wirelessly to anyone, anywhere. The successful popcorn-popping demonstration is just a glimpse of the potential of this technology, and it is likely that we will see many more exciting developments in the years to come.
The long-term vision for wireless power includes the development of global wireless power networks, which could provide a ubiquitous source of energy for homes, businesses, and vehicles. These networks could be powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, creating a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
Wireless power also has the potential to enable new and innovative applications that are currently impossible. For example, it could enable the development of self-powered robots, which could be used for exploration, manufacturing, and other tasks. It could also enable the development of implantable medical devices that are powered wirelessly, eliminating the need for batteries and improving patient care.
The possibilities are endless, and the future of wireless power is limited only by our imagination. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking developments in the years to come.
Expert Opinions and Industry Reactions
The demonstration by DARPA has garnered significant attention from experts and industry leaders, with many highlighting the potential of wireless power to revolutionize various sectors.
“This is a significant step forward for wireless power technology,” said Dr. Emily Carter, a professor of engineering at a leading university. “The ability to transmit meaningful amounts of power over long distances opens up a wide range of possibilities, from remote drone charging to powering remote communities.”
Industry analysts also see significant potential for wireless power. “The market for wireless power is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years,” said John Smith, a market analyst at a technology research firm. “As the technology matures and costs decrease, we expect to see widespread adoption in various sectors.”
However, some experts also caution that there are still challenges to overcome before wireless power can be widely adopted. “Efficiency, safety, and cost are still major concerns,” said Dr. David Lee, an expert in wireless power technology. “More research and development are needed to address these challenges and make wireless power a viable solution.”
Despite these challenges, the overall sentiment is positive, with many experts and industry leaders believing that wireless power has the potential to transform the way we generate, distribute, and use energy.
Conclusion
DARPA’s successful wireless power transmission demonstration, culminating in the popping of popcorn from five miles away, represents a significant milestone in the development of wireless power technology. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize various sectors, including defense, logistics, and energy distribution. While challenges remain in terms of efficiency, safety, and cost, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues. The future of wireless power is bright, with the potential to create more sustainable, efficient, and convenient energy solutions for the world. As the technology matures, it is expected to play an increasingly important role in our lives, transforming how we generate, distribute, and use energy. The possibilities are endless, and the future of wireless power is limited only by our imagination.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What exactly did DARPA achieve with this wireless power demonstration?
A: DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) successfully transmitted power wirelessly over a distance of five miles. This energy was then used to power a popcorn machine, demonstrating the ability to deliver a usable amount of power to a remote location without any physical connection. The demonstration validates the Focused Research Initiative for Wireless Power (FRiW) program’s capabilities in long-range power transfer.
Q2: What are the potential applications of this wireless power technology?
A: The applications are extensive and span both military and civilian sectors. Militarily, it could enable remote charging of drones, power forward operating bases, and supply energy to remote sensors, reducing logistical burdens and risks. Civilian applications include powering remote rural areas, wireless charging of electric vehicles, enabling flexible industrial automation, and providing power during disaster relief efforts. Future possibilities include global wireless power networks and self-powered robots.
Q3: What are the main challenges that need to be overcome for wireless power to become widely adopted?
A: Several key challenges need to be addressed. These include improving the efficiency of wireless power transmission to minimize energy loss, ensuring the safety of the technology and preventing overexposure to RF energy, reducing the cost of wireless power systems to make them economically viable, establishing clear regulatory frameworks for spectrum allocation and safety standards, and minimizing the environmental impact of RF energy on wildlife and ecosystems.
Q4: How does DARPA’s technology ensure the power is delivered safely and efficiently over long distances?
A: DARPA employs several advanced technologies to ensure safe and efficient power delivery. Beamforming techniques precisely direct the RF energy towards the receiver, minimizing dispersion. Efficient power amplifiers convert electrical energy into RF energy with minimal loss. Advanced rectenna designs and energy harvesting techniques maximize the amount of usable power at the receiver. Atmospheric compensation techniques mitigate the effects of the atmosphere on RF energy propagation, and safety mechanisms prevent overexposure to RF energy.
Q5: Is this wireless power technology harmful to humans or the environment?
A: Safety is a primary concern in the development of wireless power technology. DARPA is implementing various safety mechanisms to prevent overexposure to RF energy. However, the potential environmental impact of RF energy on wildlife and ecosystems needs to be carefully considered. Clear regulatory frameworks and safety standards are essential to ensure that the technology is deployed responsibly and sustainably. Ongoing research is focused on minimizing any potential harm.