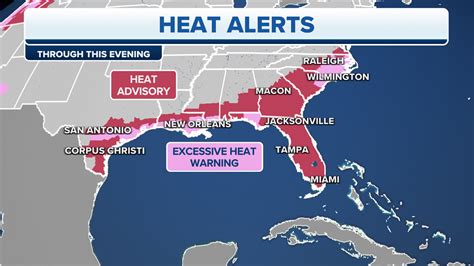
Several U.S. regions are bracing for a potentially scorching summer, with forecasts indicating above-average temperatures across much of the country and highlighting four areas at particular risk for extreme heat. The regions include parts of the Pacific Northwest, the Southwest, the South Central states, and the Northeast, where residents should prepare for prolonged periods of high temperatures and humidity.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has issued its summer outlook, predicting a high likelihood of warmer-than-average conditions for a significant portion of the United States. This forecast raises concerns about heat-related illnesses, strain on energy grids, and potential impacts on agriculture and water resources. Health officials are urging residents in the identified hotspot regions to take precautions to stay safe during the upcoming months.
Heatwave Hotspots: A Region-by-Region Breakdown
-
Pacific Northwest: The Pacific Northwest, known for its mild summers, is expected to experience higher-than-usual temperatures. This follows a trend of increasingly frequent and intense heatwaves in the region, driven by climate change. According to NOAA, there is a “greater than 50% chance of above-average temperatures” for the Pacific Northwest this summer. The increased heat poses a risk to vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those without access to air conditioning.
-
Southwest: The Southwestern states, already accustomed to high temperatures, are predicted to face an even hotter summer than normal. This includes states like Arizona, Nevada, and California, where extreme heat can exacerbate drought conditions and increase the risk of wildfires. Water scarcity is a major concern in this region, and prolonged heatwaves can put additional stress on already limited water supplies. The NOAA outlook indicates “a high probability of above-average temperatures” for the Southwest.
-
South Central States: The South Central states, including Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, and Louisiana, are also expected to endure a scorching summer. High humidity levels in this region can make the heat feel even more intense, increasing the risk of heatstroke and other heat-related illnesses. The combination of high temperatures and humidity creates a dangerous environment, particularly for those working outdoors. Experts warn that “extreme heat can significantly impact agricultural yields and livestock production” in this region.
-
Northeast: The Northeast, while typically experiencing milder summers compared to other regions, is also at risk for extreme heat this year. Urban areas in the Northeast, such as New York City and Boston, are particularly vulnerable due to the urban heat island effect, where concrete and asphalt absorb and retain heat, leading to higher temperatures compared to surrounding areas. The NOAA forecast suggests “an elevated chance of above-average temperatures” for the Northeast, prompting concerns about the health and well-being of residents.
The Science Behind the Scorching Summer
Climate change is a significant factor contributing to the increasing frequency and intensity of heatwaves around the world. As greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise, the Earth’s average temperature is increasing, leading to more extreme weather events, including heatwaves. Scientific studies have shown a clear link between climate change and the observed increase in heatwave frequency and intensity.
“The effects of climate change are becoming increasingly evident, with heatwaves becoming more common and more intense,” said Dr. Sarah Thompson, a climate scientist at the University of California, Berkeley. “We need to take urgent action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impacts of climate change and protect communities from the dangers of extreme heat.”
Public Health Concerns and Safety Measures
Extreme heat can pose serious health risks, including heatstroke, heat exhaustion, and dehydration. Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, children, and those with chronic health conditions, are particularly susceptible to heat-related illnesses. It is crucial for individuals to take precautions to stay safe during periods of extreme heat.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the following safety measures to prevent heat-related illnesses:
-
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, even if you don’t feel thirsty. Avoid sugary drinks and alcohol, which can dehydrate you.
-
Stay Cool: Seek out air-conditioned environments, such as shopping malls, libraries, or community centers. If you don’t have air conditioning at home, consider visiting a cooling center.
-
Limit Outdoor Activities: Avoid strenuous activities during the hottest part of the day. If you must be outdoors, wear lightweight, light-colored clothing and a wide-brimmed hat.
-
Check on Vulnerable Individuals: Check on elderly neighbors, friends, and family members to ensure they are staying cool and hydrated.
-
Never Leave Children or Pets in Cars: Cars can quickly heat up to dangerous temperatures, even on mild days. Never leave children or pets unattended in a vehicle.
Local governments and health organizations are also taking steps to prepare for the upcoming heatwaves. Many cities are opening cooling centers, distributing water bottles, and providing information on heat safety. Public health officials are urging residents to be aware of the risks of extreme heat and to take precautions to protect themselves and their families.
Impact on Infrastructure and Economy
Extreme heat can also have significant impacts on infrastructure and the economy. High temperatures can strain energy grids, leading to power outages. Roads and bridges can buckle under the heat, and transportation systems can be disrupted. Agricultural yields can be reduced, and livestock can suffer from heat stress.
The Texas power grid, for example, has faced challenges in recent years due to increased demand for electricity during heatwaves. In February 2021, a severe winter storm caused widespread power outages in Texas, highlighting the vulnerability of the state’s energy infrastructure. The upcoming summer heatwaves could put additional strain on the grid, increasing the risk of blackouts.
“We are working to ensure that our energy infrastructure is resilient and reliable, but extreme weather events can still pose challenges,” said John Smith, a spokesperson for the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT). “We encourage residents to conserve energy during peak demand hours to help prevent power outages.”
The agricultural sector is also vulnerable to the impacts of extreme heat. High temperatures can reduce crop yields, increase water demand, and stress livestock. Farmers may need to implement irrigation strategies and provide shade for their animals to mitigate the effects of the heat.
“Extreme heat can have a devastating impact on agricultural production,” said Mary Johnson, an agricultural economist at the University of California, Davis. “We need to develop climate-resilient farming practices to protect our food supply from the impacts of climate change.”
Long-Term Strategies for Heatwave Resilience
Addressing the challenges posed by extreme heat requires a combination of short-term and long-term strategies. In the short term, it is crucial to implement public health measures to protect vulnerable populations and ensure that energy grids are prepared to meet increased demand. In the long term, it is essential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impacts of climate change and invest in infrastructure improvements to enhance resilience to extreme weather events.
Some potential long-term strategies include:
-
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and reducing deforestation are essential steps to mitigate climate change and reduce the frequency and intensity of heatwaves.
-
Improving Urban Planning: Implementing urban planning strategies that reduce the urban heat island effect, such as planting trees and using reflective building materials, can help to lower temperatures in urban areas.
-
Investing in Infrastructure: Upgrading energy grids, water infrastructure, and transportation systems to make them more resilient to extreme weather events is crucial.
-
Developing Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Implementing farming practices that are adapted to changing climate conditions, such as drought-resistant crops and water-efficient irrigation techniques, can help to protect food security.
-
Raising Public Awareness: Educating the public about the risks of extreme heat and providing information on how to stay safe can help to reduce heat-related illnesses and deaths.
Community Preparedness and Response
Community preparedness is essential for mitigating the impacts of extreme heat. Local governments, community organizations, and individuals all have a role to play in preparing for and responding to heatwaves.
Some key aspects of community preparedness include:
-
Developing Heat Emergency Plans: Local governments should develop comprehensive heat emergency plans that outline procedures for opening cooling centers, distributing water, and providing assistance to vulnerable populations.
-
Training First Responders: First responders, such as firefighters and paramedics, should be trained to recognize and treat heat-related illnesses.
-
Establishing Cooling Centers: Cooling centers provide a safe and comfortable environment for people to escape the heat. These centers should be accessible to all residents, including those with disabilities.
-
Distributing Water and Resources: Providing water bottles, fans, and other resources to vulnerable populations can help to prevent heat-related illnesses.
-
Communicating with the Public: Local governments and community organizations should communicate with the public about the risks of extreme heat and provide information on how to stay safe.
The Role of Technology in Heatwave Management
Technology can play a significant role in managing heatwaves and mitigating their impacts. Weather forecasting models can provide early warnings of impending heatwaves, allowing communities to prepare in advance. Smart thermostats can help to conserve energy and reduce strain on the power grid. Mobile apps can provide real-time information on cooling centers and heat safety tips.
Some specific examples of technology used in heatwave management include:
-
Weather Forecasting Models: NOAA’s weather forecasting models provide detailed predictions of temperature and humidity, allowing communities to anticipate and prepare for heatwaves.
-
Smart Thermostats: Smart thermostats can automatically adjust temperatures to conserve energy and reduce strain on the power grid.
-
Mobile Apps: Mobile apps can provide real-time information on cooling centers, heat safety tips, and emergency services.
-
Remote Sensing: Remote sensing technologies, such as satellites and drones, can be used to monitor urban heat islands and identify areas that are most vulnerable to extreme heat.
Individual Responsibility and Action
While government and community efforts are crucial, individual responsibility is also essential for mitigating the impacts of extreme heat. Individuals can take steps to protect themselves and their families by staying hydrated, staying cool, limiting outdoor activities, and checking on vulnerable individuals.
Some specific actions that individuals can take include:
-
Monitoring the Weather Forecast: Pay attention to weather forecasts and be aware of impending heatwaves.
-
Staying Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, even if you don’t feel thirsty.
-
Staying Cool: Seek out air-conditioned environments or visit a cooling center.
-
Limiting Outdoor Activities: Avoid strenuous activities during the hottest part of the day.
-
Wearing Appropriate Clothing: Wear lightweight, light-colored clothing and a wide-brimmed hat.
-
Checking on Vulnerable Individuals: Check on elderly neighbors, friends, and family members to ensure they are staying cool and hydrated.
-
Conserving Energy: Conserve energy by turning off lights and appliances when not in use.
Looking Ahead: Preparing for Future Heatwaves
As climate change continues to exacerbate extreme weather events, it is crucial to prepare for future heatwaves. This requires a multi-faceted approach that includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions, investing in infrastructure improvements, implementing public health measures, and raising public awareness.
By taking proactive steps to address the challenges posed by extreme heat, we can protect our communities and build a more resilient future. The NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center offers seasonal outlooks that provide a general temperature and precipitation forecast for the upcoming months, which can be valuable for long-term planning.
The Socioeconomic Impact of Extreme Heat
Extreme heat disproportionately affects low-income communities and marginalized populations. These communities often lack access to air conditioning, healthcare, and other resources that are essential for mitigating the impacts of extreme heat. Additionally, many low-income workers are employed in outdoor occupations, making them more vulnerable to heat-related illnesses.
Addressing the socioeconomic disparities related to extreme heat requires targeted interventions that provide assistance to vulnerable populations. This may include providing access to cooling centers, offering financial assistance for energy bills, and implementing workplace safety regulations to protect outdoor workers.
“We need to ensure that all communities have the resources they need to protect themselves from the dangers of extreme heat,” said Dr. Maria Rodriguez, a public health expert at the University of Texas at Austin. “This includes investing in infrastructure improvements, providing access to healthcare, and implementing policies that protect vulnerable workers.”
The Psychological Impact of Extreme Heat
Extreme heat can also have a significant impact on mental health. High temperatures can exacerbate existing mental health conditions and increase stress, anxiety, and irritability. Prolonged exposure to extreme heat can also lead to sleep disturbances and cognitive impairment.
Addressing the psychological impacts of extreme heat requires providing mental health support to affected individuals and communities. This may include offering counseling services, promoting stress-reduction techniques, and providing information on coping strategies.
“It is important to recognize that extreme heat can have a significant impact on mental health,” said Dr. David Lee, a psychiatrist at the University of California, Los Angeles. “We need to provide mental health support to those who are struggling to cope with the challenges of extreme heat.”
International Perspectives on Heatwave Management
Heatwaves are a global phenomenon, and many countries around the world are grappling with the challenges of managing extreme heat. Some countries have implemented innovative strategies to mitigate the impacts of heatwaves, such as:
-
Heat Action Plans: Many European countries have developed heat action plans that outline procedures for responding to heatwaves. These plans typically include measures such as opening cooling centers, distributing water, and providing assistance to vulnerable populations.
-
Green Infrastructure: Some cities are investing in green infrastructure, such as parks and green roofs, to reduce the urban heat island effect.
-
Public Awareness Campaigns: Many countries are conducting public awareness campaigns to educate people about the risks of extreme heat and provide information on how to stay safe.
The Future of Heatwaves: Projections and Preparedness
Climate models project that heatwaves will become more frequent, intense, and longer-lasting in the future. This means that it is essential to take proactive steps to prepare for future heatwaves and mitigate their impacts.
Some key areas of focus for future heatwave preparedness include:
-
Improving Weather Forecasting: Investing in weather forecasting models to provide more accurate and timely warnings of impending heatwaves.
-
Developing Heat-Resilient Infrastructure: Designing and building infrastructure that is more resilient to extreme heat, such as heat-resistant roads and buildings.
-
Implementing Adaptive Strategies: Developing and implementing adaptive strategies to help communities cope with the impacts of extreme heat, such as water conservation measures and drought-resistant agriculture.
-
Strengthening International Collaboration: Collaborating with other countries to share knowledge and best practices on heatwave management.
By taking proactive steps to prepare for future heatwaves, we can protect our communities and build a more resilient future in the face of climate change. The urgency to act is clear, as the trend towards hotter summers continues to intensify. The consequences of inaction could be devastating, impacting public health, infrastructure, and the economy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Which regions in the U.S. are most likely to experience a scorching summer?
A1: According to forecasts, the regions at the highest risk for extreme heat this summer include parts of the Pacific Northwest, the Southwest, the South Central states, and the Northeast. These areas are predicted to have a higher probability of above-average temperatures.
Q2: What are the primary health risks associated with extreme heat?
A2: The primary health risks associated with extreme heat include heatstroke, heat exhaustion, dehydration, and exacerbation of existing health conditions. Vulnerable populations such as the elderly, children, and those with chronic illnesses are particularly at risk.
Q3: How can I stay safe during a heatwave?
A3: To stay safe during a heatwave, it is recommended to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, seek out air-conditioned environments, limit outdoor activities during the hottest part of the day, wear lightweight and light-colored clothing, and check on vulnerable individuals. Never leave children or pets unattended in cars.
Q4: What can be done to prepare communities for future heatwaves?
A4: Preparing communities for future heatwaves involves developing heat emergency plans, training first responders, establishing cooling centers, distributing water and resources, communicating with the public about heat safety, and investing in heat-resilient infrastructure. Long-term strategies include reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving urban planning.
Q5: What is the urban heat island effect, and why is it a concern?
A5: The urban heat island effect refers to the phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures compared to surrounding rural areas due to the concentration of buildings, roads, and other infrastructure that absorb and retain heat. This is a concern because it exacerbates the impact of heatwaves in cities, increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses and strain on energy grids.