Tesla’s long-term battery health is exceeding expectations, challenging conventional wisdom about electric vehicle battery degradation, according to recent analysis. An automotive expert has debunked widespread fears regarding rapid battery capacity loss in Tesla vehicles, citing real-world data indicating minimal degradation even after hundreds of thousands of miles.
Tesla Battery Degradation: Myth vs. Reality
Concerns about the longevity and performance of electric vehicle (EV) batteries have long been a significant barrier to wider adoption. Specifically, potential buyers often worry about how quickly a battery’s capacity will diminish over time, reducing the vehicle’s range and overall value. However, recent analysis of high-mileage Tesla vehicles suggests that these fears may be largely unfounded.
According to an automotive expert cited by Yahoo! Autos, real-world data demonstrates that Tesla batteries exhibit remarkably slow degradation rates, even after extensive use. This finding contradicts the common perception that EV batteries degrade rapidly, losing a significant portion of their capacity within a few years. “The data is showing that these batteries are lasting far longer and degrading far slower than most people, including many EV advocates, expected,” the expert stated.
Data-Driven Insights into Battery Longevity
The analysis is based on extensive data collected from Tesla owners who have driven their vehicles for significant distances. This data includes information on battery capacity, mileage, charging habits, and environmental conditions. By analyzing this data, the expert was able to identify trends and patterns in battery degradation rates.
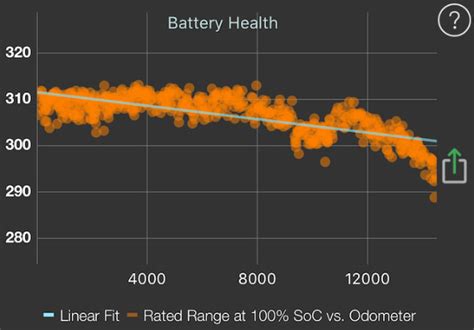
The key finding is that Tesla batteries typically retain a high percentage of their original capacity even after exceeding 200,000 miles. While some degradation is inevitable, the rate at which it occurs is significantly lower than many people anticipate. “We’re seeing batteries with over 200,000 miles still retaining 85% to 90% of their original capacity,” the expert noted.
This level of performance has significant implications for the long-term cost of ownership of Tesla vehicles. If batteries last longer and degrade more slowly, owners can expect to replace them less frequently, reducing their overall maintenance expenses. It also enhances the resale value of these EVs, making them a more attractive option for prospective buyers.
Factors Influencing Battery Degradation
While the data indicates that Tesla batteries are generally robust, certain factors can influence the rate at which they degrade. These factors include:
- Charging Habits: Frequent fast charging, especially using high-voltage DC fast chargers, can accelerate battery degradation. This is because fast charging generates more heat, which can stress the battery cells.
- Operating Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can also impact battery performance and longevity. High temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions within the battery, leading to faster degradation. Conversely, cold temperatures can reduce battery capacity and performance.
- State of Charge (SoC): Maintaining a battery at very high or very low states of charge for extended periods can also contribute to degradation. Ideally, it’s best to keep the battery within a moderate SoC range (e.g., 20% to 80%) to minimize stress.
- Driving Style: Aggressive driving habits, such as frequent acceleration and hard braking, can put more strain on the battery and potentially accelerate degradation.
Tesla’s Battery Management System (BMS)
One of the key reasons for Tesla’s impressive battery performance is its sophisticated Battery Management System (BMS). The BMS is a complex electronic system that monitors and controls various aspects of battery operation, including:
- Cell Balancing: The BMS ensures that all the individual battery cells within the pack are balanced in terms of voltage and charge. This helps to prevent overcharging or undercharging of individual cells, which can lead to premature degradation.
- Temperature Management: The BMS actively manages the battery’s temperature, using cooling and heating systems to keep it within an optimal operating range. This helps to minimize the impact of extreme temperatures on battery performance and longevity.
- Charge Control: The BMS controls the charging process, ensuring that the battery is charged safely and efficiently. It also prevents overcharging, which can damage the battery.
- Fault Detection: The BMS constantly monitors the battery for any signs of problems or faults. If a fault is detected, the BMS can take corrective action, such as shutting down the charging process or alerting the driver.
The BMS plays a crucial role in protecting the battery from damage and optimizing its performance. It is one of the key factors that differentiate Tesla’s batteries from those of other EV manufacturers.
Implications for the EV Market
The findings regarding Tesla’s battery longevity have significant implications for the broader EV market. They help to alleviate concerns about the long-term cost of ownership of EVs and make them a more attractive option for consumers. As battery technology continues to improve and manufacturers refine their battery management systems, the lifespan and performance of EV batteries are likely to increase even further.
This will further accelerate the adoption of EVs and help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector. The debunking of the battery degradation myth is a positive development for the EV industry and a significant step towards a more sustainable transportation future.
Expert Commentary
The automotive expert emphasized that the observed battery degradation is often linear, meaning that the rate of capacity loss remains relatively constant over time. This is in contrast to some earlier assumptions that battery degradation would accelerate as the battery aged. “What we’re seeing is a fairly linear degradation curve,” the expert explained. “The initial drop-off is minimal, and then it continues at a fairly consistent rate.”
This linear degradation pattern is good news for EV owners, as it means that they can more accurately predict the remaining lifespan of their battery. It also suggests that the battery will continue to provide useful service for many years, even after it has lost some of its original capacity.
Beyond Tesla: General EV Battery Trends
While the specific analysis focused on Tesla vehicles, the general trends in EV battery technology are encouraging for the entire industry. Battery manufacturers are continuously working to improve battery chemistry, cell design, and manufacturing processes. These advancements are leading to batteries with higher energy density, longer lifespans, and lower costs.
For example, solid-state batteries are a promising technology that could potentially offer significant improvements in energy density and safety. Solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid electrolyte found in traditional lithium-ion batteries. This eliminates the risk of electrolyte leakage and allows for the use of more energy-dense materials.
The Role of Software Updates
Tesla’s ability to remotely update its vehicles’ software also plays a role in battery management. These updates can include improvements to the BMS, charging algorithms, and thermal management systems. By continuously refining its software, Tesla can optimize battery performance and extend its lifespan.
This is a significant advantage over traditional automakers, who typically require owners to bring their vehicles into a service center for software updates. Tesla’s over-the-air update capability allows it to quickly and easily deploy improvements to its entire fleet of vehicles.
Addressing Range Anxiety
One of the biggest barriers to EV adoption is range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station. However, the increasing lifespan and performance of EV batteries are helping to alleviate this concern. As batteries last longer and provide more range, drivers can feel more confident about taking longer trips without worrying about running out of power.
In addition, the charging infrastructure is constantly expanding, with more and more public charging stations being installed every year. This makes it easier for EV owners to find a place to charge their vehicles when they are away from home.
Future Outlook
The future of EV batteries looks bright. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more improvements in battery performance, lifespan, and cost. This will make EVs even more attractive to consumers and further accelerate their adoption.
The debunking of the battery degradation myth is a significant step in this direction. It helps to dispel misconceptions about EV batteries and demonstrates that they are a reliable and long-lasting technology. As more people become aware of the true capabilities of EV batteries, we can expect to see a continued shift towards electric transportation.
Environmental Benefits
The widespread adoption of EVs has significant environmental benefits. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which helps to reduce air pollution in urban areas. In addition, EVs can be powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, which further reduces their carbon footprint.
By transitioning to electric transportation, we can significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and help to combat climate change. The long lifespan of EV batteries is a key factor in achieving these environmental benefits, as it ensures that these vehicles can provide clean transportation for many years.
Economic Considerations
The shift to electric transportation also has significant economic implications. The EV industry is creating new jobs in manufacturing, research and development, and infrastructure development. In addition, EVs can help to reduce our dependence on foreign oil, which strengthens our national security and improves our trade balance.
The long lifespan of EV batteries is a key factor in making EVs economically viable. As batteries last longer and cost less, EVs become more competitive with traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. This will further accelerate their adoption and create new economic opportunities.
Conclusion
The analysis of Tesla’s high-mileage vehicles provides compelling evidence that EV batteries are more durable and long-lasting than many people believe. The debunking of the battery degradation myth is a positive development for the EV industry and a significant step towards a more sustainable transportation future.
As battery technology continues to improve and manufacturers refine their battery management systems, the lifespan and performance of EV batteries are likely to increase even further. This will make EVs even more attractive to consumers and further accelerate their adoption. The future of transportation is electric, and the long lifespan of EV batteries is a key factor in making this vision a reality. FAQ: Tesla Battery Longevity and Degradation
1. How much battery degradation can I expect from my Tesla over time?
According to recent analysis, Tesla batteries degrade at a remarkably slow rate. While some degradation is inevitable, data from high-mileage vehicles suggests that you can expect to retain a significant percentage of your original battery capacity even after hundreds of thousands of miles. “We’re seeing batteries with over 200,000 miles still retaining 85% to 90% of their original capacity,” as one expert noted. The degradation is also often linear, meaning the rate of capacity loss remains relatively constant over time. However, actual degradation can vary depending on driving habits, charging habits, and environmental factors.
2. What factors can influence the rate of battery degradation in a Tesla?
Several factors can influence the rate at which a Tesla battery degrades:
- Charging Habits: Frequent use of DC fast chargers, especially high-voltage ones, can accelerate degradation due to the heat generated during charging.
- Operating Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can negatively impact battery performance and longevity.
- State of Charge (SoC): Consistently maintaining the battery at very high or very low SoC levels can contribute to degradation. Aim to keep the battery within a moderate range (e.g., 20% to 80%).
- Driving Style: Aggressive driving with frequent acceleration and hard braking can put more strain on the battery.
3. How does Tesla’s Battery Management System (BMS) contribute to battery longevity?
Tesla’s sophisticated BMS plays a crucial role in protecting the battery and optimizing its performance. The BMS performs several key functions:
- Cell Balancing: Ensures all individual battery cells are balanced in voltage and charge to prevent overcharging or undercharging.
- Temperature Management: Actively manages battery temperature using cooling and heating systems to maintain an optimal operating range.
- Charge Control: Controls the charging process to ensure safe and efficient charging and prevents overcharging.
- Fault Detection: Constantly monitors the battery for any signs of problems and takes corrective action if needed.
These functions help to minimize stress on the battery and extend its lifespan.
4. Is it better to charge my Tesla to 100% or stop at a lower percentage to preserve battery health?
Generally, it’s recommended to avoid consistently charging your Tesla to 100% unless you need the full range for a specific trip. Regularly charging to 100% can put extra stress on the battery and potentially accelerate degradation. For daily driving, charging to 80% or 90% is often sufficient and can help prolong battery life. Tesla’s owner’s manual provides specific recommendations for optimal charging practices based on the battery type in your vehicle.
5. What happens to my Tesla battery at the end of its life? Is it recycled?
Tesla is committed to recycling its batteries at the end of their useful life in vehicles. The company has developed its own battery recycling processes to recover valuable materials such as lithium, nickel, cobalt, and aluminum. These materials can then be used to manufacture new batteries, reducing the need for raw material extraction. Tesla also partners with third-party recyclers to ensure that batteries are recycled responsibly and sustainably. The goal is to create a closed-loop system where battery materials are continuously reused.









