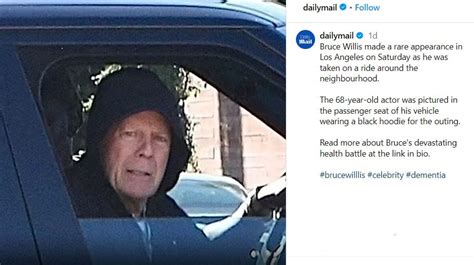
Bruce Willis, 70, was recently seen publicly for the first time in months, sparking a flurry of reactions from fans and reigniting discussions about his health and well-being following his frontotemporal dementia (FTD) diagnosis. The appearance prompted both supportive messages and concerns about the actor’s condition.
Bruce Willis, the beloved action star, made a rare public appearance recently, marking his first sighting in several months. The sighting, which quickly spread across social media, has ignited a widespread discussion among fans, raising both concerns and supportive messages regarding his health and well-being. Willis, who turned 70 in March, was diagnosed with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) last year, leading to his retirement from acting.
The details surrounding the sighting remain scarce, but the fact that Willis was seen publicly at all has provided a glimpse into his life post-diagnosis. Frontotemporal dementia is a group of brain disorders that primarily affect the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. These areas are generally associated with personality, behavior, and language. As a result, FTD can cause significant changes in these areas, leading to difficulties in communication, decision-making, and emotional regulation.
Since his diagnosis was made public, Willis’s family has been open about his condition, providing updates and raising awareness about FTD. His wife, Emma Heming Willis, and his ex-wife, Demi Moore, along with his children, have been vocal advocates for research and support for those affected by the disease. This public support has been instrumental in destigmatizing dementia and fostering a sense of community among those facing similar challenges.
The recent sighting has amplified these efforts, bringing renewed attention to FTD and the impact it has on individuals and their families. Fans have taken to social media to express their love and support for Willis, sharing memories of his iconic roles and sending well wishes to him and his family. At the same time, there is an undercurrent of concern, with many expressing sadness at seeing the once-vigorous action star battling such a debilitating condition.
The circumstances of Willis’s appearance have not been fully disclosed, including where and when the sighting occurred, and who he was with at the time. These details have been intentionally kept private to protect Willis’s privacy and allow him to live his life with dignity. The family has emphasized the importance of respecting his boundaries and allowing him to navigate his illness with the support of his loved ones.
The impact of Willis’s diagnosis extends beyond his personal life, impacting the entertainment industry and raising awareness about the challenges faced by individuals living with dementia. His legacy as an actor remains untarnished, and his work continues to be celebrated by fans around the world. By sharing his story, Willis and his family have provided a valuable service to the community, shedding light on a condition that is often misunderstood and stigmatized.
The outpouring of support following the recent sighting underscores the deep connection that fans have with Willis and his work. He remains an iconic figure in Hollywood, known for his tough-guy persona and his memorable performances in films like “Die Hard,” “Pulp Fiction,” and “The Sixth Sense.” His contributions to the film industry have earned him numerous accolades and a lasting place in popular culture.
As Willis continues to navigate his illness, his family remains committed to providing him with the best possible care and support. They have also expressed gratitude for the outpouring of love and support from fans around the world. By raising awareness about FTD, they hope to inspire others to learn more about the condition and to support research efforts aimed at finding better treatments and ultimately a cure.
The recent sighting of Bruce Willis serves as a reminder of the human toll of dementia and the importance of compassion and understanding. It also highlights the power of community and the ability of individuals to come together to support those in need. As Willis continues his journey, he can take comfort in knowing that he is surrounded by love and that his story is making a difference in the lives of others.
In-Depth Analysis of Bruce Willis’s Situation
Bruce Willis’s diagnosis with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) has not only profoundly impacted his personal life but has also reverberated throughout the entertainment industry and the broader community. FTD is a particularly cruel disease, characterized by progressive damage to the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. These areas are crucial for regulating behavior, personality, language, and executive functions. Unlike Alzheimer’s disease, which primarily affects memory, FTD often manifests with marked changes in personality and social behavior, leading to difficulties in maintaining relationships and performing daily tasks.
The specific type of FTD that Willis is battling has not been publicly disclosed, but there are several subtypes, each with its own set of symptoms and progression. Behavioral variant FTD (bvFTD) is characterized by changes in personality and behavior, such as impulsivity, disinhibition, apathy, and loss of social awareness. Language variants of FTD, such as progressive nonfluent aphasia (PNFA) and semantic dementia, affect language abilities, leading to difficulties with speech, comprehension, and word finding.
The challenges faced by individuals with FTD and their families are significant. There is currently no cure for FTD, and treatment options are limited to managing symptoms and providing supportive care. This often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including medication to address behavioral symptoms, speech therapy to improve communication, and occupational therapy to help with daily activities.
The impact on caregivers is particularly profound. Caring for someone with FTD can be emotionally and physically draining, as the disease can lead to significant behavioral changes and require constant supervision. Caregivers often experience stress, burnout, and feelings of isolation. Support groups and respite care can provide valuable resources for caregivers, allowing them to connect with others who understand their challenges and to take breaks from their caregiving responsibilities.
The openness of Willis’s family in sharing his diagnosis has been instrumental in raising awareness about FTD and destigmatizing dementia. By speaking candidly about his condition, they have provided a valuable service to the community, helping to educate the public about the disease and to reduce the stigma associated with it. Their advocacy has also inspired others to share their stories and to connect with support organizations.
The entertainment industry has also responded to Willis’s diagnosis with an outpouring of support. Many of his colleagues and collaborators have expressed their admiration for his talent and their sympathy for his situation. This has helped to raise awareness about FTD within the industry and to encourage greater understanding and compassion for those affected by the disease.
The long-term implications of Willis’s diagnosis are uncertain. FTD is a progressive disease, and its course can vary significantly from person to person. However, with proper care and support, individuals with FTD can maintain their quality of life and continue to engage in meaningful activities. The focus is on maximizing their abilities and providing them with a supportive and loving environment.
The recent sighting of Bruce Willis serves as a poignant reminder of the human cost of dementia. It also highlights the importance of early diagnosis, comprehensive care, and ongoing research. By raising awareness about FTD, Willis and his family are helping to pave the way for better treatments and ultimately a cure. Their courage and advocacy are an inspiration to others facing similar challenges.
Background Information on Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is not a single disease but rather a group of brain disorders that primarily affect the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. These areas are responsible for essential functions such as personality, behavior, language, and executive functions (planning, decision-making, and problem-solving). FTD is less common than Alzheimer’s disease, accounting for approximately 10-20% of all dementia cases. However, it tends to affect people at a younger age, typically between the ages of 40 and 65.
The exact cause of FTD is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. In some cases, FTD is caused by mutations in specific genes, such as MAPT, GRN, and C9orf72. These genes play a role in the production of proteins that are essential for the normal functioning of brain cells. When these genes are mutated, they can lead to the accumulation of abnormal proteins in the brain, which can damage and kill brain cells.
There are several different subtypes of FTD, each with its own set of symptoms and progression. The most common subtypes include:
- Behavioral variant FTD (bvFTD): This subtype is characterized by changes in personality and behavior, such as impulsivity, disinhibition, apathy, loss of social awareness, and compulsive behaviors. Individuals with bvFTD may also experience difficulties with executive functions, such as planning, decision-making, and problem-solving.
- Progressive nonfluent aphasia (PNFA): This subtype affects language abilities, leading to difficulties with speech production. Individuals with PNFA may struggle to form sentences, speak fluently, or find the right words to express themselves. They may also have difficulties with grammar and syntax.
- Semantic dementia: This subtype also affects language abilities, but it primarily affects comprehension. Individuals with semantic dementia may have difficulty understanding the meaning of words, recognizing objects, or understanding social cues. They may also experience changes in personality and behavior, such as increased rigidity and difficulty with abstract thinking.
The diagnosis of FTD can be challenging, as its symptoms can overlap with those of other neurological and psychiatric disorders. A thorough evaluation typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, neuropsychological testing, and brain imaging. Neuropsychological testing can help to assess cognitive functions such as memory, language, and executive functions. Brain imaging techniques, such as MRI and PET scans, can help to identify structural and functional abnormalities in the brain.
There is currently no cure for FTD, and treatment options are limited to managing symptoms and providing supportive care. Medications may be used to address behavioral symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and agitation. Speech therapy can help to improve communication skills. Occupational therapy can help with daily activities.
Caring for someone with FTD can be a challenging and demanding task. Caregivers often experience stress, burnout, and feelings of isolation. Support groups and respite care can provide valuable resources for caregivers, allowing them to connect with others who understand their challenges and to take breaks from their caregiving responsibilities.
Research into FTD is ongoing, with the goal of developing better treatments and ultimately a cure. Current research efforts are focused on understanding the underlying causes of FTD, identifying new biomarkers for early diagnosis, and developing new therapies to target the disease process.
The Impact on Bruce Willis’s Career and Legacy
Bruce Willis’s illustrious career in Hollywood spans decades, marked by a string of memorable performances in a variety of genres. From his breakthrough role as David Addison in the television series “Moonlighting” to his iconic portrayal of John McClane in the “Die Hard” franchise, Willis has captivated audiences with his charisma, wit, and action-hero prowess.
His contributions to the film industry have earned him numerous accolades, including a Golden Globe Award and an Emmy Award. He has also been nominated for several other awards, including a Saturn Award for Best Actor.
Beyond his commercial success, Willis has also been praised for his versatility as an actor. He has demonstrated his ability to excel in both comedic and dramatic roles, showcasing his range and depth as a performer. Some of his most notable performances include his roles in “Pulp Fiction,” “The Sixth Sense,” “12 Monkeys,” and “Sin City.”
Willis’s diagnosis with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) has brought an end to his acting career, but his legacy as one of Hollywood’s most beloved and respected actors remains intact. His films continue to be enjoyed by audiences around the world, and his contributions to the entertainment industry will not be forgotten.
The decision to retire from acting was undoubtedly a difficult one for Willis, but it was made in the best interests of his health and well-being. FTD is a progressive disease that can significantly impair cognitive and physical abilities, making it increasingly difficult to perform complex tasks such as acting.
By stepping away from the spotlight, Willis has been able to focus on his health and spend time with his family. His family has been a constant source of support throughout his journey, providing him with love, care, and understanding.
The outpouring of support from fans and colleagues following his diagnosis underscores the deep connection that people have with Willis and his work. He remains an iconic figure in Hollywood, and his contributions to the film industry will continue to be celebrated for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Bruce Willis’s Health and FTD
-
What is frontotemporal dementia (FTD)?
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a group of brain disorders that primarily affect the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. These areas are responsible for personality, behavior, language, and executive functions (planning, decision-making, and problem-solving). FTD can cause significant changes in these areas, leading to difficulties in communication, decision-making, and emotional regulation. “Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is an umbrella term for a group of brain disorders that primarily affect the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. These areas of the brain are generally associated with personality, behavior and language,” as defined by the original article.
-
What are the symptoms of FTD?
The symptoms of FTD can vary depending on the specific areas of the brain that are affected. Common symptoms include changes in personality and behavior, such as impulsivity, disinhibition, apathy, loss of social awareness, and compulsive behaviors. Other symptoms may include difficulties with speech, comprehension, word finding, and executive functions.
-
Is there a cure for FTD?
Unfortunately, there is currently no cure for FTD. Treatment options are limited to managing symptoms and providing supportive care. Medications may be used to address behavioral symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and agitation. Speech therapy can help to improve communication skills. Occupational therapy can help with daily activities.
-
How is FTD diagnosed?
The diagnosis of FTD can be challenging, as its symptoms can overlap with those of other neurological and psychiatric disorders. A thorough evaluation typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, neuropsychological testing, and brain imaging. Neuropsychological testing can help to assess cognitive functions such as memory, language, and executive functions. Brain imaging techniques, such as MRI and PET scans, can help to identify structural and functional abnormalities in the brain.
-
What kind of support is available for people with FTD and their families?
Caring for someone with FTD can be a challenging and demanding task. Caregivers often experience stress, burnout, and feelings of isolation. Support groups and respite care can provide valuable resources for caregivers, allowing them to connect with others who understand their challenges and to take breaks from their caregiving responsibilities. Organizations such as The Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration (AFTD) also provide information, resources, and support for individuals with FTD and their families.
Expanded Context: The Role of Media and Public Perception
The media’s role in reporting on Bruce Willis’s health condition has been a delicate balance between providing informative updates and respecting his privacy. The initial announcement of his aphasia diagnosis and subsequent revelation of FTD brought widespread attention to these conditions, educating the public about lesser-known neurological disorders. However, the intensity of media coverage also raises questions about the ethical considerations of reporting on a public figure’s personal health struggles.
The public’s perception of Willis’s condition has been shaped by media narratives, social media discussions, and the family’s openness in sharing updates. The outpouring of support and well-wishes demonstrates a collective empathy for Willis and his family, reflecting a growing awareness and understanding of dementia-related illnesses. This heightened awareness can contribute to reducing the stigma associated with dementia and encouraging more open conversations about mental and neurological health.
However, the media’s portrayal of Willis’s condition can also inadvertently reinforce negative stereotypes or create unrealistic expectations about the progression of FTD. It’s crucial for media outlets to provide accurate and nuanced information, avoiding sensationalism or oversimplification of complex medical conditions. Additionally, respecting the privacy of individuals with dementia and their families is paramount, ensuring that their dignity and autonomy are preserved.
The Willis family’s decision to share their journey with FTD has been a significant factor in shaping public perception. By being transparent about the challenges and realities of the condition, they have empowered others to share their own experiences and seek support. Their advocacy efforts have also contributed to raising funds for research and promoting awareness about FTD, making a tangible difference in the lives of those affected by the disease.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Reporting on Health Information
Reporting on the health conditions of public figures like Bruce Willis involves navigating complex legal and ethical considerations. While the public has a legitimate interest in the well-being of celebrities, their right to privacy must also be respected. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States protects the privacy of individuals’ medical information, but it primarily applies to healthcare providers and insurance companies, not the media.
However, ethical journalism principles dictate that reporters should avoid intruding on individuals’ privacy and should only publish information that is newsworthy and in the public interest. In the case of Bruce Willis, the announcement of his aphasia and FTD diagnoses met this criteria because it provided valuable information about these conditions and raised awareness about the challenges faced by individuals and families affected by dementia.
When reporting on health information, journalists must also ensure accuracy and avoid sensationalism. Medical information should be obtained from reliable sources, such as medical professionals or reputable organizations. It’s crucial to avoid making speculative claims or exaggerating the severity of a condition. Additionally, journalists should be sensitive to the emotional impact of their reporting on individuals and families affected by health conditions.
The legal and ethical considerations surrounding reporting on health information can vary depending on the jurisdiction. Some countries have stricter privacy laws than others. Journalists should be aware of the laws and ethical guidelines in their respective regions and should consult with legal counsel when necessary.
The Future of FTD Research and Treatment
Research into frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a rapidly evolving field, with significant progress being made in understanding the underlying causes of the disease and developing new treatments. Current research efforts are focused on several key areas:
- Genetics: Identifying genes that increase the risk of FTD and understanding how these genes contribute to the disease process.
- Biomarkers: Developing biomarkers that can be used to diagnose FTD early and track its progression.
- Pathophysiology: Investigating the mechanisms by which FTD damages brain cells and identifying potential therapeutic targets.
- Therapeutics: Developing new drugs and other therapies that can slow or stop the progression of FTD.
Several promising therapeutic approaches are currently being investigated in clinical trials. These include:
- Antibody therapies: Antibodies that target abnormal proteins in the brain, such as tau and TDP-43.
- Gene therapies: Gene therapies that aim to correct genetic mutations that cause FTD.
- Small molecule drugs: Small molecule drugs that target specific pathways involved in the disease process.
While a cure for FTD remains elusive, the progress being made in research offers hope for the future. With continued investment in research and innovation, it is likely that more effective treatments for FTD will be developed in the coming years. This will improve the quality of life for individuals with FTD and their families, and ultimately lead to a cure for this devastating disease.
The Importance of Support Organizations and Advocacy
Support organizations and advocacy groups play a crucial role in supporting individuals with FTD and their families, raising awareness about the disease, and advocating for research funding and policy changes. These organizations provide a range of services, including:
- Information and education: Providing accurate and up-to-date information about FTD to individuals, families, and healthcare professionals.
- Support groups: Facilitating support groups for individuals with FTD and their caregivers, providing a safe and supportive environment to share experiences and connect with others.
- Respite care: Providing respite care services to caregivers, allowing them to take breaks from their caregiving responsibilities.
- Advocacy: Advocating for research funding, policy changes, and increased awareness about FTD.
The Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration (AFTD) is the leading organization dedicated to FTD in the United States. AFTD provides a wide range of resources and support services to individuals with FTD and their families, and advocates for research and policy changes. Other organizations that provide support for individuals with dementia and their families include the Alzheimer’s Association and the Lewy Body Dementia Association.
By supporting these organizations and advocating for increased awareness and research funding, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by FTD and help to accelerate the development of new treatments and ultimately a cure. The awareness brought forth by Bruce Willis’ diagnosis and the continuous support from his family, combined with dedicated organizations, offer a beacon of hope for those battling FTD.









