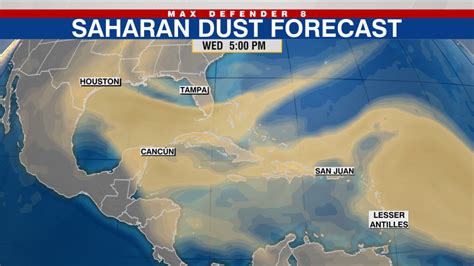
A massive plume of Saharan dust is traversing the Atlantic Ocean and expected to reach the United States, potentially impacting air quality and suppressing storm development. The dust cloud, originating from the Sahara Desert in Africa, is anticipated to arrive in the Gulf Coast region and parts of the Southeast, bringing with it hazy skies and vibrant sunsets, but also posing respiratory concerns for sensitive individuals. While the dust’s arrival could temporarily reduce the likelihood of tropical cyclones, its impact is complex and multifaceted.
A large-scale Saharan Air Layer (SAL), a mass of dry, dusty air that forms over the Sahara Desert during the late spring, summer, and early fall, is currently making its way across the Atlantic Ocean towards the United States. This phenomenon is not unusual, occurring several times each year, but the size and density of this particular dust cloud have garnered attention. According to experts, the dust cloud is already affecting air quality in the Caribbean and is expected to reach the U.S. mainland in the coming days, impacting regions stretching from Texas to Florida. The primary concerns associated with the dust cloud are related to air quality and potential health impacts, particularly for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions such as asthma and allergies. While the dust can create picturesque sunrises and sunsets, its presence also signifies a deterioration in air quality that can exacerbate respiratory problems.
The Saharan Air Layer is characterized by its extreme dryness, elevated altitudes, and high dust concentration. The dry air associated with the SAL can suppress storm formation by inhibiting the development of thunderstorms, which are necessary for tropical cyclone development. The dust particles themselves can also interfere with cloud formation and rainfall, further reducing the likelihood of storm activity. However, it’s crucial to note that the presence of the SAL is just one factor influencing hurricane formation, and other atmospheric and oceanic conditions also play a significant role.
The arrival of the Saharan dust cloud is expected to bring several notable effects to the affected regions of the United States. Foremost among these is the expected degradation of air quality. The dust particles, which are very fine, can easily be inhaled and penetrate deep into the lungs, potentially triggering or worsening respiratory problems. Individuals with asthma, allergies, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other respiratory ailments are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of the dust. Health officials advise these individuals to take precautions, such as staying indoors, using air purifiers, and avoiding strenuous outdoor activities, especially during periods of high dust concentration.
Beyond the health impacts, the dust cloud is also expected to affect visibility. The dust particles scatter sunlight, leading to hazy skies and reduced visibility. This can impact transportation, particularly air travel, as reduced visibility can make it more challenging for pilots to navigate. Motorists may also experience reduced visibility, particularly during sunrise and sunset, when the dust scatters light more intensely.
One of the most visually striking effects of the Saharan dust cloud is the creation of vibrant sunrises and sunsets. The dust particles scatter sunlight, particularly the shorter wavelengths of blue and green light, allowing the longer wavelengths of red and orange light to pass through more easily. This results in more intense and colorful sunrises and sunsets, which can be a beautiful sight to behold. However, it’s important to remember that these picturesque displays come at the cost of degraded air quality.
While the Saharan dust cloud is primarily known for its negative impacts, such as reduced air quality and visibility, it also has some potential benefits. One of these is the suppression of hurricane formation. The dry air associated with the SAL can inhibit the development of thunderstorms, which are necessary for tropical cyclone formation. The dust particles themselves can also interfere with cloud formation and rainfall, further reducing the likelihood of storm activity. While the SAL is not a foolproof preventative measure against hurricanes, it can play a role in reducing the frequency and intensity of these storms.
Another potential benefit of the Saharan dust cloud is the fertilization of ecosystems. The dust particles contain minerals and nutrients that can be beneficial to plant life. When the dust settles, these minerals and nutrients are deposited on the land and in the ocean, where they can act as fertilizers, promoting plant growth and supporting marine ecosystems.
The relationship between Saharan dust and hurricane activity is complex and not fully understood. While the dry air and dust particles associated with the SAL can suppress storm formation, other atmospheric and oceanic conditions also play a significant role. Factors such as sea surface temperatures, wind shear, and atmospheric instability can all influence hurricane development, and the presence of the SAL is just one piece of the puzzle.
Some studies have suggested that the SAL can reduce the frequency and intensity of hurricanes, while others have found little or no correlation. It’s important to note that hurricane formation is a complex process influenced by a multitude of factors, and the SAL is just one of them. While the arrival of the Saharan dust cloud may temporarily reduce the likelihood of tropical cyclones, it’s not a guarantee that hurricanes will not form.
The Saharan Air Layer typically forms over the Sahara Desert during the late spring, summer, and early fall. During this time, intense solar heating of the desert surface creates a layer of hot, dry air that rises into the atmosphere. This air is also laden with dust particles, which are lifted into the air by strong winds. The resulting mass of hot, dry, dusty air is known as the Saharan Air Layer.
The SAL is transported westward across the Atlantic Ocean by the prevailing trade winds. As it travels, it gradually cools and mixes with the surrounding air, but it can still maintain its distinct characteristics for thousands of miles. When the SAL reaches the Caribbean and the United States, it can have a variety of impacts, including reduced air quality, hazy skies, vibrant sunrises and sunsets, and the suppression of hurricane formation.
The size and intensity of the Saharan dust cloud can vary from year to year, depending on factors such as the amount of dust available in the Sahara Desert, the strength of the trade winds, and the atmospheric conditions over the Atlantic Ocean. Some years, the dust clouds are relatively small and have little impact on the Caribbean and the United States. Other years, the dust clouds are much larger and more intense, and they can have significant impacts on air quality, visibility, and hurricane formation.
The current dust cloud is considered to be larger and denser than average, which is why it has garnered so much attention. Experts are monitoring the dust cloud closely to track its progress and assess its potential impacts. They are also working to improve our understanding of the relationship between Saharan dust and hurricane activity, so that we can better predict the impacts of future dust clouds.
The National Weather Service and other meteorological agencies use a variety of tools and techniques to monitor the Saharan Air Layer and track its movement across the Atlantic Ocean. These tools include satellites, weather models, and ground-based observations.
Satellites are used to monitor the dust cloud from space. They can provide information on the size, density, and location of the dust cloud. Weather models are used to predict the movement of the dust cloud and its potential impacts. These models take into account factors such as wind speed and direction, temperature, and humidity. Ground-based observations, such as air quality monitors and visibility sensors, are used to measure the impacts of the dust cloud on the ground.
By combining these different sources of information, meteorologists can provide accurate and timely forecasts of the Saharan Air Layer and its potential impacts. This information can be used to help people prepare for the arrival of the dust cloud and take steps to protect their health.
The health impacts of the Saharan dust cloud are primarily related to respiratory problems. The dust particles, which are very fine, can easily be inhaled and penetrate deep into the lungs. This can trigger or worsen respiratory problems, such as asthma, allergies, and COPD.
Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of the dust. They may experience symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. In some cases, exposure to the dust can lead to hospitalization or even death.
Even healthy individuals can experience respiratory irritation from exposure to the dust. They may experience symptoms such as a scratchy throat, runny nose, and irritated eyes.
To protect your health during the arrival of the Saharan dust cloud, health officials recommend the following:
- Stay indoors as much as possible, especially during periods of high dust concentration.
- Use air purifiers to filter the air inside your home.
- Avoid strenuous outdoor activities, such as running and gardening.
- If you must go outside, wear a dust mask or respirator.
- Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
- If you have asthma or allergies, make sure you have your medications with you and use them as prescribed.
- If you experience any respiratory symptoms, such as coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath, seek medical attention.
The Saharan dust cloud can also have impacts on transportation. The dust particles scatter sunlight, leading to hazy skies and reduced visibility. This can impact air travel, as reduced visibility can make it more challenging for pilots to navigate. Motorists may also experience reduced visibility, particularly during sunrise and sunset, when the dust scatters light more intensely.
To protect yourself while driving during the arrival of the Saharan dust cloud, follow these tips:
- Slow down and increase your following distance.
- Use your headlights, even during the day.
- Be aware of your surroundings and watch out for other vehicles and pedestrians.
- If visibility is severely reduced, pull over to the side of the road and wait for the dust to clear.
The Saharan dust cloud is a natural phenomenon that occurs several times each year. While it can have some negative impacts, such as reduced air quality and visibility, it also has some potential benefits, such as the suppression of hurricane formation and the fertilization of ecosystems.
By understanding the Saharan dust cloud and its potential impacts, we can take steps to protect our health and safety. We can also appreciate the beauty of the vibrant sunrises and sunsets that the dust cloud can create.
As the dust cloud continues its journey across the Atlantic, meteorologists will continue to monitor its progress and provide updates on its potential impacts. It is crucial for residents in affected areas to stay informed and take necessary precautions to minimize the negative effects of the Saharan dust. The dust’s arrival serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of our global environment and the far-reaching consequences of natural phenomena. The Saharan dust’s journey across the Atlantic is a testament to the power of wind and the ability of the atmosphere to transport particles over vast distances.
The intensity of the Saharan Air Layer events varies from year to year and can be influenced by climate patterns and changes in land use in the Sahara region. Monitoring these events helps scientists understand broader climate patterns and their potential effects on weather and climate around the world. Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term impacts of these dust clouds on ecosystems, human health, and climate. This includes studying the chemical composition of the dust and its interaction with other atmospheric pollutants. The Saharan dust serves as an important reminder of the need for global cooperation in monitoring and addressing environmental challenges. Understanding the sources, transport pathways, and impacts of dust particles is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their negative effects and harness their potential benefits.
The study of Saharan dust and its impacts is an ongoing area of research, with scientists continually working to improve our understanding of this complex phenomenon. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more detailed and accurate monitoring of dust clouds, leading to better predictions and more effective strategies for managing their impacts. This includes developing new methods for forecasting dust events, assessing their impacts on human health, and mitigating their negative effects.
The Saharan dust also carries microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi, across the Atlantic. The viability and ecological impact of these transported microorganisms are areas of ongoing research. There is concern about the potential spread of pathogens and allergens via Saharan dust clouds. Scientists are studying the types of microorganisms transported in the dust and their potential effects on human and animal health. The dust can also affect marine ecosystems by depositing iron and other nutrients into the ocean, which can stimulate phytoplankton growth. However, excessive dust deposition can also lead to harmful algal blooms and other ecological problems.
The Saharan dust cloud also affects cloud formation and precipitation patterns. The dust particles can act as cloud condensation nuclei, influencing the size and number of cloud droplets. This can affect the amount of precipitation that falls from clouds. The impact of Saharan dust on cloud formation and precipitation is complex and depends on a variety of factors, including the type of dust particles, the atmospheric conditions, and the presence of other pollutants.
The Saharan dust cloud is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon with a wide range of impacts on human health, ecosystems, and climate. By understanding the sources, transport pathways, and impacts of dust particles, we can develop more effective strategies for mitigating their negative effects and harnessing their potential benefits. This requires a multidisciplinary approach involving meteorologists, atmospheric scientists, ecologists, and public health experts.
The Saharan dust cloud serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of our global environment and the importance of understanding the complex interactions between different parts of the Earth system. As we continue to study this phenomenon, we can gain valuable insights into the workings of our planet and the challenges we face in managing our environment. The monitoring and study of Saharan dust also provide opportunities for international collaboration and data sharing. By working together, scientists from different countries can improve our understanding of this phenomenon and develop more effective strategies for mitigating its impacts.
The potential impact of the dust cloud is influenced by various factors, including the size and density of the dust plume, wind patterns, and local weather conditions. Accurate forecasting of these events relies on sophisticated atmospheric models and real-time monitoring data. The dust clouds can vary significantly in their properties, affecting the intensity of their impacts. It is also crucial to note that the long-term effects of these dust events on ecosystems and human health are still under investigation.
The arrival of the Saharan dust cloud highlights the need for proactive measures to protect public health and minimize environmental impacts. This includes providing timely information to the public, implementing air quality monitoring programs, and developing strategies for managing dust emissions.
The impacts of the Saharan dust cloud are felt across a wide range of sectors, including public health, agriculture, transportation, and tourism. Effective management of these impacts requires a coordinated approach involving government agencies, businesses, and the public. The Saharan dust cloud also serves as a reminder of the importance of addressing the root causes of desertification and land degradation in the Sahara region. These efforts can help to reduce the amount of dust that is lifted into the atmosphere and transported across the Atlantic.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is Saharan dust, and where does it come from?
Saharan dust is a mixture of sand, silt, and clay particles lifted into the atmosphere from the Sahara Desert in North Africa. “The Saharan Air Layer (SAL) is a mass of very dry, dusty air that forms over the Sahara Desert during the late spring, summer, and early fall, and then it moves over the Atlantic.” These particles are carried westward across the Atlantic Ocean by trade winds.
-
How does Saharan dust affect air quality in the United States?
The dust particles can significantly degrade air quality. According to the Yahoo News article, the primary concerns are related to air quality and potential health impacts, particularly for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions. These fine particles can be inhaled deeply into the lungs, potentially triggering or exacerbating respiratory problems like asthma and allergies.
-
Can Saharan dust impact hurricane formation?
Yes, the Saharan Air Layer is known to suppress hurricane formation. “The dry air associated with the SAL can inhibit the development of thunderstorms, which are necessary for tropical cyclone development. The dust particles themselves can also interfere with cloud formation and rainfall, further reducing the likelihood of storm activity.” However, it is essential to note that this is just one factor; other atmospheric and oceanic conditions also play a significant role.
-
What precautions should people take when Saharan dust arrives in their area?
Health officials recommend several precautions: “staying indoors, using air purifiers, and avoiding strenuous outdoor activities, especially during periods of high dust concentration.” Individuals with respiratory conditions should be particularly vigilant and have their medications readily available.
-
Are there any positive aspects to Saharan dust clouds?
While primarily known for negative impacts, Saharan dust can have some benefits. One is “the fertilization of ecosystems. The dust particles contain minerals and nutrients that can be beneficial to plant life.” When the dust settles, these minerals can enrich soil and marine environments.
-
How long does the Saharan dust cloud typically last in the US?
The duration of the Saharan dust cloud’s presence in the US varies depending on several factors, including the size and density of the plume, wind patterns, and atmospheric conditions. Generally, the effects of the dust cloud can last from a few days to a week or more. The initial arrival of the dust can bring the most noticeable impacts, such as hazy skies and reduced air quality. Over time, the dust particles gradually settle out of the atmosphere or are dispersed by wind and weather systems. The persistence of the dust cloud can also depend on whether there are subsequent plumes following behind the initial one. If additional dust clouds are transported across the Atlantic, they can prolong the period of reduced air quality and hazy conditions. Meteorologists and air quality experts monitor the dust cloud closely to track its movement and provide forecasts on its expected duration. Residents in affected areas should stay informed about the latest updates and follow any recommendations from health officials. The cyclical nature of Saharan dust events means that similar occurrences can be expected in the late spring, summer, and early fall months.
- What are the long-term effects of repeated exposure to Saharan dust?
The long-term effects of repeated exposure to Saharan dust are an area of ongoing research. While short-term exposure can cause respiratory irritation and exacerbate existing conditions, the cumulative effects of repeated exposure over many years are less well understood. Some studies suggest that chronic exposure to fine particulate matter, including dust, can contribute to the development of respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues. The mineral composition of the dust particles can also play a role in their long-term health impacts. Some dust particles may contain toxic substances or allergens that can trigger adverse reactions in sensitive individuals. The frequency and intensity of Saharan dust events can vary from year to year, making it challenging to assess the long-term health consequences. More research is needed to fully understand the potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. This includes studying the health outcomes of populations that are repeatedly exposed to Saharan dust and developing air quality standards that take into account the unique characteristics of dust particles.
- How do climate change and land use practices affect Saharan dust events?
Climate change and land use practices can both influence the frequency and intensity of Saharan dust events. Changes in temperature, rainfall patterns, and vegetation cover can affect the amount of dust that is available for transport into the atmosphere. For example, prolonged droughts can lead to increased desertification and land degradation, making it easier for wind to lift dust particles. Deforestation and unsustainable agricultural practices can also contribute to soil erosion and dust emissions. Climate change can also alter wind patterns and atmospheric circulation, which can affect the transport and dispersal of dust clouds. Some studies suggest that climate change may lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as dust storms, in the Sahara region. However, the relationship between climate change, land use, and Saharan dust events is complex and not fully understood. More research is needed to assess the long-term impacts and develop strategies to mitigate the negative effects of dust emissions. This includes promoting sustainable land management practices, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and implementing measures to adapt to the changing climate.
- Are there any measures being taken to reduce dust emissions from the Sahara Desert?
While it is challenging to completely eliminate dust emissions from the Sahara Desert, there are several measures that can be taken to reduce them. These include:
- Sustainable land management: Implementing practices that prevent soil erosion and land degradation, such as afforestation, reforestation, and conservation tillage.
- Water management: Using water resources more efficiently to prevent desertification and maintain vegetation cover.
- Climate change mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow down the pace of climate change and prevent further desertification.
- Early warning systems: Developing systems to forecast dust storms and provide timely warnings to affected populations.
- International cooperation: Working with countries in the Sahara region to implement sustainable land management practices and reduce dust emissions.
These measures require a coordinated effort involving governments, international organizations, and local communities. While it may not be possible to completely eliminate dust emissions from the Sahara Desert, these efforts can help to reduce their frequency and intensity and mitigate their negative impacts.
- What is the role of technology in monitoring and forecasting Saharan dust events?
Technology plays a crucial role in monitoring and forecasting Saharan dust events. Satellites, weather models, and ground-based observations are all used to track the movement of dust clouds and assess their potential impacts. Satellites provide a broad overview of dust plumes from space, allowing scientists to monitor their size, density, and location. Weather models use complex algorithms to simulate atmospheric processes and predict the movement of dust clouds. These models take into account factors such as wind speed and direction, temperature, and humidity. Ground-based observations, such as air quality monitors and visibility sensors, provide real-time measurements of dust concentrations and visibility conditions. By combining these different sources of information, meteorologists can provide accurate and timely forecasts of Saharan dust events. These forecasts can be used to help people prepare for the arrival of dust clouds and take steps to protect their health. Advances in technology are continually improving our ability to monitor and forecast Saharan dust events. This includes the development of new satellite sensors, more sophisticated weather models, and improved data assimilation techniques. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more accurate and reliable forecasts of Saharan dust events, leading to better preparedness and reduced impacts.
- Can Saharan dust affect aviation and air travel?
Yes, Saharan dust can significantly affect aviation and air travel. The dust particles in the air reduce visibility, making it difficult for pilots to navigate, especially during takeoff and landing. Reduced visibility can lead to flight delays, diversions, and even cancellations. Dust particles can also damage aircraft engines. When ingested into the engine, the dust can cause abrasion and erosion of the engine components, leading to reduced performance and increased maintenance costs. The fine dust particles can also clog air filters and sensors, affecting the aircraft’s instrumentation and control systems. Airlines and aviation authorities take several precautions to mitigate the risks posed by Saharan dust. These include:
- Adjusting flight schedules: Delaying or canceling flights when dust concentrations are high.
- Using specialized aircraft: Using aircraft with engines that are more resistant to dust ingestion.
- Improving air filtration systems: Installing more efficient air filters to prevent dust from entering the aircraft.
- Providing pilot training: Training pilots to fly in dusty conditions and recognize the signs of engine damage.
- Monitoring dust conditions: Monitoring dust concentrations and visibility conditions at airports.
By taking these precautions, airlines and aviation authorities can help to ensure the safety of air travel during Saharan dust events. Passengers should be aware of the potential for delays and cancellations and should check with their airlines for the latest information.
- What is the impact of Saharan dust on marine ecosystems?
Saharan dust plays a complex role in marine ecosystems. On one hand, it can provide essential nutrients, such as iron, that stimulate phytoplankton growth. Phytoplankton are microscopic plants that form the base of the marine food web. Iron is often a limiting nutrient in ocean waters, so the addition of iron from Saharan dust can boost phytoplankton production. This can have cascading effects throughout the food web, supporting larger organisms, such as fish and marine mammals. On the other hand, excessive dust deposition can also have negative impacts on marine ecosystems. It can lead to harmful algal blooms, which can produce toxins that kill fish and other marine life. Dust can also smother coral reefs and other sensitive habitats. The impact of Saharan dust on marine ecosystems depends on a variety of factors, including the amount and composition of the dust, the oceanographic conditions, and the sensitivity of the ecosystem. Scientists are studying the complex interactions between Saharan dust and marine ecosystems to better understand their effects and develop strategies to mitigate any negative impacts.
- How does the composition of Saharan dust vary, and why is it important?
The composition of Saharan dust can vary depending on the source region within the Sahara Desert and the atmospheric processes that it undergoes during transport. The dust typically contains a mixture of minerals, including quartz, feldspar, clay minerals, and iron oxides. The relative proportions of these minerals can vary depending on the geological composition of the source region. The composition of Saharan dust is important for several reasons. First, it affects the dust’s ability to absorb and scatter sunlight. Minerals like iron oxides can absorb sunlight, which can warm the atmosphere and affect cloud formation. Second, the composition of the dust can influence its impact on human health. Some minerals may be more toxic or allergenic than others. Third, the composition of the dust can affect its ability to fertilize ecosystems. Different minerals contain different nutrients that can be beneficial to plant life. Scientists use various techniques to analyze the composition of Saharan dust, including X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy, and chemical analysis. By understanding the composition of the dust, they can better predict its impacts on climate, human health, and ecosystems.
- Are there economic impacts associated with Saharan dust events?
Yes, there are several economic impacts associated with Saharan dust events. These impacts can be felt across a range of sectors, including:
- Aviation: As mentioned earlier, Saharan dust can cause flight delays, diversions, and cancellations, which can lead to significant economic losses for airlines and airports.
- Tourism: Hazy skies and reduced visibility can deter tourists from visiting affected areas, leading to decreased revenue for hotels, restaurants, and other tourism-related businesses.
- Agriculture: Dust deposition can both benefit and harm agriculture. While the dust can provide essential nutrients to crops, excessive dust deposition can also smother plants and reduce yields.
- Healthcare: Increased respiratory problems can lead to higher healthcare costs, including doctor visits, hospitalizations, and medication expenses.
- Construction: Dust can interfere with construction activities, leading to delays and increased costs.
The economic impacts of Saharan dust events can be significant, especially in regions that are frequently affected. Governments and businesses can take steps to mitigate these impacts, such as implementing air quality monitoring programs, providing timely information to the public, and developing strategies to protect sensitive industries.
- How can individuals stay informed about the arrival of Saharan dust clouds in their area?
Individuals can stay informed about the arrival of Saharan dust clouds in their area by monitoring several sources of information:
- National Weather Service: The National Weather Service (NWS) provides forecasts and advisories on air quality and visibility conditions, including information about Saharan dust events.
- Air Quality Agencies: State and local air quality agencies monitor air pollution levels and provide real-time data to the public. Many agencies also issue alerts and advisories when air quality is poor.
- News Media: Local news outlets often report on the arrival of Saharan dust clouds and provide information about their potential impacts.
- Online Resources: Several websites and apps provide information about air quality and dust conditions, such as AirNow, PurpleAir, and Plume Labs.
By monitoring these sources of information, individuals can stay informed about the arrival of Saharan dust clouds in their area and take steps to protect their health.