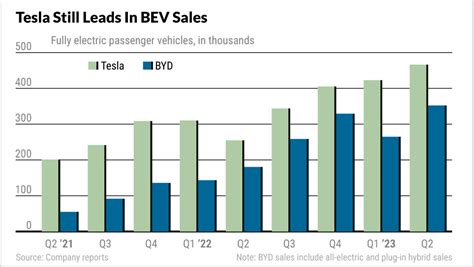
BYD’s recent price cuts across its electric vehicle (EV) lineup have sent shockwaves through the Chinese EV market, triggering a significant downturn in the stock prices of major EV manufacturers, including BYD itself, Li Auto, and Xpeng. The aggressive pricing strategy signals intensified competition and potential margin erosion within the world’s largest EV market.
Shares of BYD, the Warren Buffett-backed automotive giant, initially fell before recovering slightly, while Li Auto and Xpeng experienced more substantial declines. This market reaction underscores investor concerns about the sustainability of profitability in an environment where price wars are becoming increasingly prevalent. The price adjustments, impacting a range of BYD models, reflect the company’s strategy to maintain its dominant market share amid slowing demand growth and heightened competition from both domestic rivals and Tesla.
The price reductions vary depending on the model, with some EVs seeing cuts of several thousand dollars, making them more accessible to a broader range of consumers. This move is aimed at stimulating sales volume and further solidifying BYD’s position as a market leader, even if it means sacrificing some short-term profitability. The company is leveraging its vertically integrated supply chain, including its in-house battery production capabilities, to absorb some of the impact of these price reductions.
Price Cuts Spark Market Jitters
The EV market in China has been a hotbed of activity in recent years, with numerous companies vying for a piece of the rapidly growing pie. However, the pace of growth has begun to moderate, partly due to broader economic concerns and shifting consumer sentiment. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly turning to price cuts as a way to attract buyers and maintain sales momentum.
“The EV sector in China is entering a new phase of maturity, where scale and efficiency are becoming paramount,” said one industry analyst. “Companies that can effectively manage costs and offer competitive pricing will be best positioned to succeed in the long run.”
BYD’s decision to implement price cuts is seen by some as a preemptive move to stay ahead of the competition. The company has consistently invested in research and development, allowing it to produce high-quality EVs at a competitive cost. By lowering prices, BYD hopes to increase its sales volume and gain further market share, potentially squeezing out smaller players in the process.
However, the move also raises concerns about the overall health of the EV industry in China. If other manufacturers are forced to follow suit and cut prices, it could lead to a race to the bottom, where profitability is severely compromised. This could make it more difficult for companies to invest in future product development and innovation.
Competitive Landscape Intensifies
The EV market in China is characterized by intense competition, with both established automakers and new entrants vying for market share. Tesla, the US-based EV giant, has been a major player in the Chinese market for several years, and its presence has forced domestic manufacturers to step up their game.
In addition to Tesla, there are numerous other EV brands competing in China, including NIO, Geely’s Zeekr, and numerous smaller companies. This crowded market makes it challenging for any one company to maintain a dominant position.
The Chinese government has been a strong supporter of the EV industry, providing subsidies and other incentives to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles. However, these subsidies have been gradually phased out, putting more pressure on manufacturers to compete on price and quality.
The price cuts implemented by BYD are likely to further intensify the competition in the Chinese EV market. Other manufacturers may feel compelled to respond with their own price reductions, which could lead to a period of price wars and margin erosion.
BYD’s Strategic Maneuvering
BYD’s aggressive pricing strategy reflects a calculated effort to maintain its leading position in the face of growing competition and moderating demand. The company’s vertically integrated supply chain, which includes in-house battery production, provides it with a cost advantage over some of its rivals. This allows BYD to offer lower prices without significantly sacrificing profitability.
Furthermore, BYD has been expanding its product lineup in recent years, offering a range of EVs to suit different consumer needs and preferences. This diversification helps the company to attract a broader customer base and reduce its reliance on any one particular model.
BYD’s global ambitions also play a role in its pricing strategy. The company is actively expanding its presence in overseas markets, including Europe and Southeast Asia. By offering competitive prices, BYD hopes to gain market share in these regions and establish itself as a global EV leader.
Impact on Li Auto and Xpeng
The stock prices of Li Auto and Xpeng, two other prominent Chinese EV manufacturers, experienced more significant declines than BYD following the announcement of the price cuts. This reflects investor concerns about the ability of these companies to compete effectively in a price-sensitive market.
Li Auto, which focuses on extended-range electric vehicles (EREVs), has seen rapid growth in recent years. However, the company’s reliance on a single technology (EREVs) makes it potentially vulnerable to shifts in consumer preferences or technological advancements.
Xpeng, which emphasizes advanced technology and autonomous driving features, has also been growing rapidly. However, the company has faced challenges in scaling up production and reducing costs.
The price cuts implemented by BYD are likely to put pressure on Li Auto and Xpeng to lower their own prices, which could impact their profitability and future growth prospects. These companies may need to find ways to differentiate themselves from BYD, such as by offering unique features or focusing on niche markets.
Tesla’s Response
Tesla, the US-based EV giant, has been a major player in the Chinese market for several years. The company’s Shanghai Gigafactory produces vehicles for both the Chinese market and export to other regions.
Tesla has also been known to adjust its prices in response to market conditions. It remains to be seen how Tesla will react to the price cuts implemented by BYD. The company could choose to match the price reductions, which would further intensify the competition in the Chinese EV market. Alternatively, Tesla could maintain its prices and focus on its brand reputation and advanced technology.
Tesla’s strategy will likely depend on its assessment of the long-term prospects for the Chinese EV market and its own competitive advantages.
Long-Term Implications
The price cuts implemented by BYD highlight the challenges and opportunities facing the EV industry in China. While lower prices can stimulate demand and accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles, they can also put pressure on manufacturers’ profitability and ability to invest in future innovation.
The long-term success of EV companies in China will depend on their ability to effectively manage costs, differentiate themselves from competitors, and adapt to changing market conditions. Companies that can achieve scale, efficiency, and innovation will be best positioned to thrive in the long run.
The Chinese government’s policies will also play a significant role in shaping the future of the EV industry. Government subsidies and regulations can help to accelerate the transition to electric vehicles, but they can also create distortions in the market.
Analyst Perspectives
“BYD’s price cuts are a clear signal that the Chinese EV market is becoming increasingly competitive,” said a senior analyst at a leading investment bank. “Companies will need to be very disciplined in managing costs and focusing on efficiency to succeed.”
Another analyst noted that “the price cuts could lead to a shakeout in the EV industry, with smaller players struggling to compete.”
Some analysts believe that the price cuts are a temporary phenomenon, driven by short-term market conditions. They argue that as demand for EVs continues to grow, prices will eventually stabilize.
Other analysts are more cautious, warning that the price cuts could be a sign of a longer-term trend towards lower profitability in the EV industry.
Consumer Impact
The price cuts implemented by BYD are undoubtedly good news for consumers. Lower prices make EVs more accessible to a wider range of buyers, which can help to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles.
However, consumers should also be aware of the potential implications of price wars. If manufacturers are forced to cut prices too deeply, it could lead to compromises in quality or features.
Consumers should also consider the long-term cost of ownership when evaluating EVs. While the initial purchase price may be lower, EVs typically have lower running costs due to lower fuel and maintenance expenses.
Global Context
The trends in the Chinese EV market have implications for the global automotive industry. China is the world’s largest market for electric vehicles, and developments in China often have a ripple effect around the world.
The increasing competitiveness of Chinese EV manufacturers is forcing automakers in other countries to step up their game. Companies that can’t compete on price and quality risk losing market share to Chinese rivals.
The global EV industry is undergoing a period of rapid change and disruption. The price cuts implemented by BYD are just one example of the forces that are shaping the future of the automotive industry.
BYD’s Recovery and Market Dynamics
Despite the initial dip in share prices following the price cut announcement, BYD’s stock showed some resilience, staging a partial recovery. This suggests that investors recognize BYD’s inherent strengths, including its scale, technological capabilities, and vertically integrated supply chain.
The recovery also reflects a broader understanding that BYD’s price cuts are not a sign of weakness but rather a strategic maneuver to maintain market dominance. BYD is betting that its ability to absorb lower margins, combined with increased sales volume, will ultimately result in stronger overall financial performance.
However, the market remains volatile, and the long-term impact of the price cuts on BYD and other EV manufacturers is still uncertain. Factors such as government policies, consumer demand, and technological innovation will all play a role in shaping the future of the Chinese EV market.
The Role of Government Policy
The Chinese government has played a critical role in the development of the EV industry, providing subsidies, tax breaks, and other incentives to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles. However, these subsidies have been gradually phased out, putting more pressure on manufacturers to compete on their own merits.
The government’s policies are now focused on promoting innovation, improving charging infrastructure, and addressing other barriers to EV adoption. The government also has a strong interest in ensuring that the EV industry remains competitive and sustainable.
The government’s policies could have a significant impact on the future of the Chinese EV market. For example, if the government were to introduce new regulations that favor domestic manufacturers, it could make it more difficult for foreign companies like Tesla to compete.
Technological Innovation
Technological innovation is another key driver of the EV market. Companies that can develop more efficient batteries, faster charging systems, and more advanced autonomous driving features will have a significant competitive advantage.
BYD has been investing heavily in research and development, and it has made significant progress in areas such as battery technology and electric powertrain systems. The company is also exploring new technologies such as solid-state batteries and wireless charging.
Other EV manufacturers are also investing heavily in research and development. The race to develop the next generation of EV technologies is likely to be intense.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why did BYD implement price cuts on its EVs?
- BYD implemented price cuts to maintain its market share and stimulate sales volume amid slowing demand growth and increased competition in the Chinese EV market. The cuts are part of a strategy to make its EVs more accessible to a broader range of consumers, leveraging its cost advantages derived from a vertically integrated supply chain.
Q2: What impact did BYD’s price cuts have on other EV stocks in China?
- The price cuts triggered a significant downturn in the stock prices of major EV manufacturers, including Li Auto and Xpeng. Investors are concerned about the potential for margin erosion in the EV industry as companies engage in price wars to attract customers.
Q3: How is BYD able to offer lower prices compared to its competitors?
- BYD benefits from a vertically integrated supply chain, including in-house battery production, which gives it greater control over costs and allows it to offer competitive pricing without sacrificing profitability significantly.
Q4: How might Tesla respond to BYD’s price cuts in China?
- Tesla could respond by matching BYD’s price cuts to maintain its market share, which would further intensify competition. Alternatively, Tesla might maintain its prices, focusing on its brand reputation, advanced technology, and the value proposition it offers to consumers.
Q5: What are the long-term implications of price wars in the Chinese EV market?
- While price cuts can benefit consumers by making EVs more affordable, they can also lead to reduced profitability for manufacturers and potentially hinder investment in research and development. The long-term success of EV companies will depend on their ability to manage costs, differentiate their products, and adapt to the evolving market conditions. A price war can also result in a shakeout, where smaller players struggle to compete and may be forced to exit the market.
The Chinese EV market remains dynamic and highly competitive. BYD’s price cuts represent a significant development that could reshape the industry landscape. The response from other manufacturers, including Tesla, and the long-term implications for profitability and innovation will be closely watched by investors and industry observers alike. The EV sector is experiencing a maturation, and only the most agile, efficient, and innovative companies will thrive.
Expanded Analysis of Key Players
To fully understand the ramifications of BYD’s price cuts, it is crucial to delve deeper into the individual strategies and positions of the major players: BYD, Li Auto, Xpeng, and Tesla. Each company possesses unique strengths and weaknesses that will determine their ability to navigate the increasingly competitive Chinese EV market.
-
BYD: The Cost Leader
BYD’s strength lies in its vertically integrated supply chain. Unlike many of its competitors who rely on external suppliers for critical components like batteries, BYD manufactures its own batteries through its subsidiary, FinDreams Battery. This allows BYD to control costs more effectively and respond more nimbly to market changes. The company also boasts a broad product portfolio, ranging from affordable compact EVs to premium SUVs, catering to a diverse range of consumer preferences. BYD’s aggressive pricing strategy is a testament to its cost leadership and its willingness to sacrifice short-term profits for long-term market dominance. Furthermore, BYD’s commitment to plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) gives it an advantage in regions where charging infrastructure is less developed. This dual approach of offering both battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and PHEVs provides consumers with more choices and addresses range anxiety concerns.
-
Li Auto: The Range Extender
Li Auto differentiates itself with its extended-range electric vehicles (EREVs). These vehicles combine a battery-electric powertrain with a gasoline-powered range extender, effectively eliminating range anxiety while still providing a primarily electric driving experience. This approach has resonated particularly well with consumers in areas where charging infrastructure is limited or unreliable. However, Li Auto’s reliance on EREVs makes it vulnerable to potential regulatory changes or technological advancements that could favor BEVs. Furthermore, the increased complexity of EREVs, compared to BEVs, could result in higher production costs. Li Auto must continue to innovate and adapt its product strategy to maintain its competitive edge in the face of evolving market trends. The company’s focus on large, family-oriented SUVs has also been a key differentiator, appealing to a specific segment of the market.
-
Xpeng: The Technology Innovator
Xpeng positions itself as a technology innovator, focusing on advanced autonomous driving features and intelligent cockpit technology. The company has invested heavily in research and development, aiming to deliver a superior driving experience through cutting-edge technology. Xpeng’s vehicles are equipped with sophisticated sensors and software, enabling features such as autonomous parking, lane keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control. However, the development and deployment of autonomous driving technology is a costly and complex undertaking. Xpeng must demonstrate the reliability and safety of its autonomous driving features to gain consumer trust and regulatory approval. Furthermore, the company faces intense competition from other automakers, including Tesla, who are also vying for leadership in the autonomous driving space. Xpeng’s partnership with Volkswagen to jointly develop EVs for the Chinese market could provide a significant boost to its technological capabilities and market reach.
-
Tesla: The Brand Powerhouse
Tesla’s strength lies in its strong brand reputation and its advanced technology. The company has cultivated a loyal following of customers who are drawn to its sleek designs, innovative features, and over-the-air software updates. Tesla’s Shanghai Gigafactory has enabled it to produce vehicles locally, reducing costs and improving delivery times. However, Tesla faces increasing competition from domestic automakers who are offering comparable EVs at lower prices. The company’s reliance on a direct-to-consumer sales model also limits its reach in some areas where traditional dealerships are still dominant. Tesla’s Supercharger network provides a significant advantage in terms of charging infrastructure, but the company must continue to expand its network to meet the growing demand for EV charging. Tesla’s decision to offer Megapack energy storage solutions to Chinese businesses signals a diversification strategy that could further strengthen its presence in the market.
The Broader Economic Context
The Chinese EV market is not operating in isolation. Broader economic trends and government policies play a significant role in shaping the industry’s trajectory. The slowing economic growth in China, coupled with rising raw material costs, is putting pressure on EV manufacturers to reduce prices. Government policies, such as purchase incentives and infrastructure investments, can significantly impact consumer demand for EVs. Furthermore, international trade relations and geopolitical tensions can also affect the EV market, particularly with regards to supply chains and access to key technologies.
The ongoing global chip shortage has also impacted the EV industry, leading to production delays and increased costs. EV manufacturers must diversify their supply chains and secure access to critical components to mitigate the risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
The Future of the Chinese EV Market
The Chinese EV market is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, driven by increasing consumer demand, government support, and technological innovation. However, the market is also becoming increasingly competitive, with numerous players vying for market share. The price cuts initiated by BYD are a clear indication of the intensified competition.
The long-term success of EV manufacturers in China will depend on their ability to adapt to the changing market conditions, manage costs effectively, and differentiate themselves from competitors. Companies that can achieve scale, efficiency, and innovation will be best positioned to thrive in the long run.
The shift towards electric vehicles is not just a trend in China; it is a global phenomenon. The Chinese EV market is at the forefront of this transformation, and the lessons learned in China will have implications for the global automotive industry.
The interplay of pricing strategies, technological advancements, and government policies will ultimately determine the winners and losers in the Chinese EV market. The coming years will be a crucial period for EV manufacturers as they navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by this rapidly evolving landscape.
The sustainability of the industry also hinges on addressing environmental concerns related to battery production and disposal. Responsible sourcing of raw materials and the development of efficient battery recycling technologies are essential for ensuring the long-term viability of the EV industry.









