China’s strategic approach to trade is holding global markets in suspense, with stock performances heavily reliant on Beijing’s next move in ongoing trade discussions. Investors are keenly awaiting concrete policy signals and strategic decisions from China that could significantly impact market sentiment and future trade dynamics.
Global stocks are experiencing a period of stagnation as investors await definitive actions from Beijing regarding its trade strategies. The uncertainty surrounding China’s next steps is creating a cautious environment, with markets refraining from significant movements until a clearer picture emerges. The anticipation of Beijing’s strategic decisions is a critical factor influencing investor confidence and market direction.
According to analysts, the current market lull reflects a broader hesitancy stemming from unclear signals from China. “The market is in a wait-and-see mode,” noted a leading market strategist, emphasizing the dependence of market momentum on Beijing’s forthcoming announcements. This state of limbo underscores the significant influence of China’s policy decisions on global financial markets.
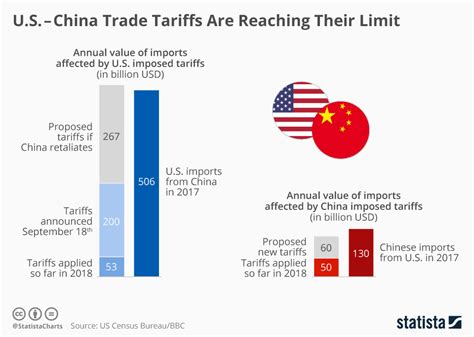
The ongoing trade negotiations between China and its key economic partners, including the United States and the European Union, are at a critical juncture. These discussions aim to address trade imbalances, intellectual property rights, and market access issues, which have been points of contention for years. The outcomes of these negotiations are expected to shape the future of international trade relations and global economic growth.
China’s approach to trade is multifaceted, balancing its domestic economic needs with its international commitments. The country is navigating a complex landscape, striving to maintain its economic growth while addressing concerns raised by its trading partners. This balancing act is crucial for sustaining China’s role as a major player in the global economy and fostering stable international trade relations.
The anticipation surrounding Beijing’s next move is palpable across various sectors, including technology, manufacturing, and agriculture. These sectors are particularly vulnerable to shifts in trade policies and are closely monitoring developments in trade negotiations. The potential impact on supply chains, tariffs, and market access is driving a cautious approach among businesses operating in these industries.
Investors are closely analyzing various indicators to gauge China’s potential policy direction. These include statements from government officials, economic data releases, and signals from state-controlled media. The ability to interpret these signals accurately is essential for making informed investment decisions and navigating the uncertainties of the current market environment.
The global implications of China’s trade decisions extend beyond financial markets, affecting geopolitical dynamics and international relations. Trade is a key component of China’s foreign policy, and its decisions can influence its relationships with other countries. Therefore, the outcomes of trade negotiations are not only economic but also political, shaping the broader landscape of international cooperation and competition.
As the world awaits Beijing’s next move, the focus remains on the potential for either positive breakthroughs or further escalations in trade tensions. The coming weeks are expected to be pivotal in determining the direction of global trade and the performance of financial markets. The decisions made by China will have far-reaching consequences for the global economy and international relations.
Deep Dive into China’s Trade Strategy
China’s trade strategy is currently at a crucial juncture, requiring a comprehensive analysis of the factors influencing Beijing’s decisions. The country’s economic objectives, domestic pressures, and international obligations all play a significant role in shaping its approach to trade negotiations and policy implementation.
Economic Objectives
China’s primary economic objective is to sustain its growth trajectory while transitioning to a more sustainable and balanced development model. This involves reducing reliance on exports, promoting domestic consumption, and fostering innovation-driven growth. Trade policies must align with these broader economic goals, supporting the development of key industries and enhancing China’s competitiveness in the global market.
The country is also focused on upgrading its manufacturing sector, moving towards higher value-added products and advanced technologies. This transition requires strategic trade policies that support technological innovation, protect intellectual property rights, and facilitate access to global markets for high-tech products.
Domestic Pressures
China faces several domestic pressures that influence its trade strategy. These include the need to create jobs, address income inequality, and manage environmental challenges. Trade policies must consider these social and economic factors, ensuring that the benefits of trade are shared more equitably across the population.
Moreover, China’s leadership is committed to maintaining social stability and addressing public concerns about the impact of trade on local industries and employment. This requires careful management of trade liberalization, with policies designed to mitigate potential negative effects and support affected communities.
International Obligations
As a major player in the global economy, China has international obligations to uphold the rules-based trading system and promote fair trade practices. This includes complying with World Trade Organization (WTO) regulations, engaging in constructive dialogue with trading partners, and addressing concerns about trade imbalances and intellectual property rights.
China is also committed to playing a more active role in global governance, contributing to the reform of the WTO and promoting multilateral cooperation on trade-related issues. This involves working with other countries to address common challenges, such as climate change, and promoting sustainable development through trade.
Analyzing China’s Potential Moves
To anticipate China’s potential moves in trade, it is essential to analyze the various scenarios and their potential implications. These scenarios include:
-
Trade Deal Breakthrough: A comprehensive trade deal with the United States or the European Union could involve concessions on tariffs, intellectual property protection, and market access. This would likely boost investor confidence, leading to positive market reactions and increased trade flows. However, such a deal would also require China to address long-standing concerns about its trade practices and regulatory environment.
-
Continued Trade Tensions: If trade negotiations fail to yield significant progress, trade tensions could escalate, leading to increased tariffs and retaliatory measures. This would create uncertainty for businesses, disrupt supply chains, and negatively impact global economic growth. In this scenario, China might focus on strengthening its domestic economy and diversifying its trade relationships.
-
Regional Trade Agreements: China could prioritize the development of regional trade agreements, such as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), to reduce its reliance on specific trading partners and promote regional economic integration. This would involve closer cooperation with countries in Asia and the Pacific, creating new opportunities for trade and investment within the region.
-
Domestic Policy Focus: China could shift its focus towards domestic policies, such as stimulating domestic consumption, promoting innovation, and reducing reliance on exports. This would involve implementing measures to boost consumer spending, support technological development, and enhance the competitiveness of domestic industries.
Impact on Global Markets
China’s trade decisions have far-reaching implications for global markets, affecting stock prices, currency values, and commodity prices. The anticipation of Beijing’s next move is creating volatility and uncertainty, with investors closely monitoring developments in trade negotiations and policy announcements.
-
Stock Markets: Stock markets are highly sensitive to trade-related news, with positive developments leading to rallies and negative developments triggering sell-offs. Companies that rely heavily on trade with China, such as those in the technology, manufacturing, and agriculture sectors, are particularly vulnerable to trade tensions.
-
Currency Markets: Currency values are also affected by trade dynamics, with the Chinese yuan and other currencies of major trading partners experiencing fluctuations in response to trade-related news. A trade deal breakthrough could strengthen the yuan, while escalating trade tensions could weaken it.
-
Commodity Markets: Commodity prices are influenced by trade flows, with increased trade leading to higher demand and prices. Trade tensions can disrupt supply chains and reduce demand, leading to lower commodity prices.
Expert Opinions and Analysis
Several experts have weighed in on China’s trade strategy and its potential impact on global markets. According to Dr. Li Wei, a leading economist at the China Academy of Social Sciences, “China is committed to promoting win-win trade relationships and addressing concerns raised by its trading partners. However, it will also defend its legitimate interests and pursue its own development goals.”
Market analysts at Goldman Sachs have noted that “the uncertainty surrounding China’s trade policy is creating headwinds for global economic growth. A resolution of trade tensions would provide a significant boost to investor confidence and economic activity.”
The Role of Geopolitics
Geopolitics plays a crucial role in shaping China’s trade strategy. Trade is not only an economic issue but also a political one, influencing China’s relationships with other countries and its role in the global order.
China’s trade decisions are often influenced by its strategic interests, such as maintaining regional stability, promoting its geopolitical influence, and securing access to resources and markets. Trade is used as a tool to build alliances, exert influence, and advance its broader foreign policy objectives.
The Future of China’s Trade Strategy
The future of China’s trade strategy will depend on a variety of factors, including the outcomes of trade negotiations, domestic economic developments, and geopolitical dynamics. China is likely to continue to play a major role in global trade, but its approach may evolve in response to changing circumstances.
One possible scenario is that China will continue to pursue a more assertive trade policy, defending its interests and challenging the existing global order. This could lead to increased trade tensions and a more fragmented global economy.
Another scenario is that China will adopt a more cooperative approach, working with other countries to reform the global trading system and address common challenges. This would require compromise and a willingness to address concerns raised by its trading partners.
Regardless of the specific path it takes, China’s trade strategy will continue to be a major factor shaping the global economy and international relations. The decisions made by Beijing will have far-reaching consequences for businesses, investors, and policymakers around the world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, China’s trade strategy is a complex and multifaceted issue with significant implications for global markets and international relations. The anticipation surrounding Beijing’s next move is creating uncertainty and volatility, with investors closely monitoring developments in trade negotiations and policy announcements.
A comprehensive understanding of China’s economic objectives, domestic pressures, and international obligations is essential for anticipating its potential moves and navigating the challenges and opportunities presented by its trade policies. The coming weeks are expected to be pivotal in determining the direction of global trade and the performance of financial markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why are global stocks stalled pending China’s trade decisions?
Global stocks are stalled because investors are waiting for clear signals from Beijing regarding its trade policies. The uncertainty surrounding China’s next moves creates a cautious environment, as its decisions can significantly impact market sentiment and future trade dynamics. “The market is in a wait-and-see mode,” as noted by a leading market strategist, highlighting the market’s dependence on Beijing’s announcements.
2. What are the key issues being negotiated in China’s trade talks?
The key issues under negotiation include trade imbalances, intellectual property rights protection, and market access. These issues have been long-standing points of contention between China and its major trading partners, such as the United States and the European Union. Addressing these issues is crucial for fostering stable and equitable trade relations.
3. How could a trade deal breakthrough impact global markets?
A trade deal breakthrough could positively impact global markets by boosting investor confidence and increasing trade flows. Such a deal would likely involve concessions on tariffs, intellectual property protection, and market access. However, it would also require China to address concerns about its trade practices and regulatory environment, potentially leading to significant economic and regulatory reforms.
4. What are the potential consequences of continued trade tensions with China?
Continued trade tensions could escalate tariffs and retaliatory measures, creating uncertainty for businesses, disrupting supply chains, and negatively impacting global economic growth. In this scenario, China might focus on strengthening its domestic economy and diversifying its trade relationships to mitigate the impact of trade disputes. This could lead to a more fragmented global economy with increased barriers to trade and investment.
5. What role does geopolitics play in China’s trade strategy?
Geopolitics plays a crucial role, as trade is not only an economic issue but also a political one influencing China’s relationships with other countries and its position in the global order. China’s trade decisions are often influenced by strategic interests, such as maintaining regional stability, promoting its geopolitical influence, and securing access to resources and markets. Trade is a tool for building alliances and advancing foreign policy objectives.
In-Depth Analysis of China’s Economic and Political Landscape
To fully understand China’s trade strategies, it’s essential to delve into the nation’s complex economic and political landscape. China’s economic model, characterized by state-led capitalism, presents unique challenges and opportunities in global trade. The government’s extensive involvement in the economy, including state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and strategic industrial policies, shapes its trade negotiations and market access conditions.
State-Led Capitalism
China’s state-led capitalist system means that the government plays a significant role in guiding economic development through planning, investment, and regulation. This system has allowed China to achieve rapid economic growth, but it also raises concerns about unfair competition, market distortions, and preferential treatment for domestic firms.
SOEs, which operate in key sectors such as energy, telecommunications, and finance, often receive preferential treatment in terms of access to credit, subsidies, and regulatory approvals. This can give them a competitive advantage over foreign firms, creating barriers to market access and distorting trade flows.
Strategic Industrial Policies
China’s strategic industrial policies, such as “Made in China 2025,” aim to promote the development of advanced industries and reduce reliance on foreign technologies. These policies involve government support for research and development, subsidies for domestic firms, and preferential procurement policies.
While these policies can stimulate innovation and economic growth, they also raise concerns about unfair competition and intellectual property theft. Trading partners often view these policies as protectionist measures that discriminate against foreign firms and distort global trade.
Political Considerations
China’s trade policies are also shaped by political considerations, including the need to maintain social stability, promote national unity, and enhance its global influence. The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) prioritizes economic growth as a means of ensuring social stability and maintaining its legitimacy.
Trade policies are often used to achieve political objectives, such as building alliances, exerting influence, and securing access to resources. China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), for example, is a massive infrastructure development project that aims to promote economic cooperation and connectivity across Asia, Africa, and Europe. While the BRI has economic benefits, it also serves China’s strategic interests by expanding its influence and creating new markets for its goods and services.
Navigating the Complexities of Trade Negotiations
China’s unique economic and political system presents challenges for trade negotiations. Trading partners must navigate complex regulatory environments, address concerns about market distortions, and ensure fair treatment for their firms.
Intellectual Property Rights Protection
Intellectual property rights (IPR) protection is a major concern for trading partners. China has made progress in strengthening its IPR laws and enforcement, but challenges remain, including the prevalence of counterfeiting and piracy.
Trading partners often seek stronger commitments from China to protect IPR, including measures to prevent the theft of trade secrets, enforce patents and copyrights, and provide effective remedies for IPR infringement.
Market Access
Market access is another key issue in trade negotiations. China’s regulatory environment can be complex and opaque, creating barriers for foreign firms. Trading partners often seek greater transparency and predictability in China’s regulatory system, as well as greater access to key sectors such as finance, telecommunications, and healthcare.
Trade Imbalances
Trade imbalances have been a long-standing source of tension between China and its trading partners. China’s large trade surplus with the United States and the European Union has led to calls for greater reciprocity and fairer trade practices.
Addressing trade imbalances requires a multifaceted approach, including measures to increase imports, reduce export subsidies, and promote structural reforms that boost domestic consumption.
Future Scenarios and Strategic Implications
Looking ahead, several scenarios could shape China’s trade strategy and its implications for the global economy.
Scenario 1: Increased Protectionism
If trade tensions continue to escalate, China could adopt a more protectionist approach, implementing new trade barriers and prioritizing domestic industries. This could lead to a more fragmented global economy, with reduced trade flows and increased geopolitical tensions.
Scenario 2: Enhanced Regional Cooperation
China could prioritize regional trade agreements, such as the RCEP, to strengthen its economic ties with other Asian countries and reduce its reliance on Western markets. This could create a new center of economic gravity in Asia, with China playing a leading role.
Scenario 3: Global Leadership
China could seek to play a more prominent role in global governance, working with other countries to reform the WTO and address global challenges such as climate change and pandemics. This would require China to embrace greater transparency, accountability, and multilateralism.
Strategic Implications for Businesses and Investors
The uncertainty surrounding China’s trade policies presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses and investors. Companies need to carefully assess the risks and opportunities associated with trading and investing in China, and develop strategies to mitigate potential disruptions.
Diversification
Diversifying supply chains and markets can help companies reduce their reliance on China and mitigate the impact of trade tensions. This could involve sourcing goods from multiple countries, expanding sales to new markets, and investing in alternative production locations.
Innovation
Investing in innovation can help companies maintain their competitiveness and adapt to changing market conditions. This could involve developing new products and services, adopting advanced technologies, and improving efficiency.
Engagement
Engaging with policymakers and industry associations can help companies shape trade policies and advocate for their interests. This could involve participating in trade dialogues, lobbying for policy changes, and working with industry groups to address common challenges.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of China’s Trade Strategy
China’s trade strategy is a critical factor shaping the global economy and international relations. Understanding the country’s economic and political landscape, navigating the complexities of trade negotiations, and adapting to future scenarios are essential for businesses, investors, and policymakers.
As China continues to evolve as a global economic power, its trade policies will have far-reaching consequences for the world. A comprehensive and nuanced understanding of China’s trade strategy is essential for navigating the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. The strategic decisions made by Beijing will continue to be closely watched and analyzed, as they hold the key to understanding the future of global trade and economic cooperation.









