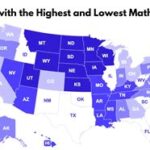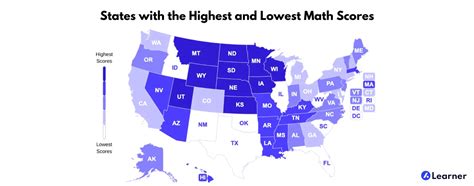
The states with the highest concentrations of residents exhibiting psychopathic traits, according to a recent study analyzing personality data, are Connecticut, Maine, and New York. The study, which examined data based on a model assessing traits like manipulativeness, deceitfulness, and recklessness, suggests a geographical distribution of these characteristics across the United States, sparking discussions about the potential societal implications and regional variations in personality profiles.
Psychopath Hotspots: Which States Score Highest on Dark Personality Traits?
A recent study has identified states with the highest concentrations of residents exhibiting psychopathic traits, revealing a potentially unsettling geographic distribution of certain dark personality characteristics across the United States. According to research, Connecticut, Maine, and New York lead the nation in the prevalence of these traits, based on an analysis utilizing a model that assesses factors such as manipulativeness, deceitfulness, and recklessness. The findings, while not indicating that the residents of these states are clinically diagnosed psychopaths, suggest a higher propensity for psychopathic-like traits within these populations compared to other states.
The study, published recently, delves into the prevalence of specific personality traits associated with psychopathy across different states. Researchers employed a data-driven approach to evaluate the presence of these characteristics, utilizing a psychometric model designed to identify individuals who exhibit tendencies towards manipulativeness, deceitfulness, recklessness, and a lack of empathy. The research methodology involved aggregating and analyzing large datasets to generate state-level scores reflecting the concentration of these traits within each population.
The states identified as having the lowest scores, indicating a lower prevalence of these traits, include West Virginia, Vermont, and North Carolina. This stark contrast between the states at the top and bottom of the list raises questions about the factors that may contribute to these regional variations in personality profiles. Socioeconomic factors, cultural differences, historical influences, and even environmental conditions could potentially play a role in shaping the prevalence of these traits within specific populations.
The implications of this study are far-reaching, touching upon various aspects of society, including crime rates, economic behavior, and political dynamics. While it is crucial to avoid generalizations and stigmatization, understanding the regional distribution of these personality traits could provide valuable insights for policymakers, law enforcement agencies, and mental health professionals. By identifying areas where these traits are more prevalent, targeted interventions and prevention programs can be developed to address potential societal challenges.
Methodology and Data Analysis
The study’s methodology relied on a comprehensive analysis of personality data collected from various sources. Researchers utilized a psychometric model designed to assess the presence and intensity of specific traits associated with psychopathy. These traits typically include:
- Manipulativeness: The tendency to exploit and deceive others for personal gain.
- Deceitfulness: A propensity for lying and dishonesty.
- Recklessness: A disregard for the safety and well-being of oneself and others.
- Lack of Empathy: An inability to understand or share the feelings of others.
- Impulsivity: Acting without thinking and making rash decisions.
- Antisocial Behavior: A pattern of disregard for social norms and rules.
The data was analyzed using statistical techniques to generate state-level scores reflecting the concentration of these traits within each population. These scores were then compared across states to identify those with the highest and lowest prevalence of psychopathic-like characteristics.
The researchers acknowledged the limitations of their study, including the reliance on self-reported data and the potential for bias in the data collection process. However, they argued that their findings provide valuable insights into the regional distribution of these personality traits and warrant further investigation.
Regional Variations and Contributing Factors
The stark contrast between the states with the highest and lowest scores on the psychopathy scale raises questions about the factors that may contribute to these regional variations in personality profiles. While the study did not explicitly investigate these factors, several potential explanations have been proposed:
- Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty, unemployment, and income inequality have been linked to increased stress, frustration, and antisocial behavior, which may contribute to the development of psychopathic-like traits. States with higher levels of socioeconomic inequality may exhibit a greater prevalence of these traits.
- Cultural Differences: Cultural norms and values can influence the expression and manifestation of personality traits. Some cultures may be more tolerant of risk-taking, aggression, and individualism, which could contribute to a higher prevalence of psychopathic-like traits.
- Historical Influences: Historical events, such as wars, economic depressions, and social unrest, can have a lasting impact on the psychological makeup of a population. States that have experienced significant historical trauma may exhibit a greater prevalence of certain personality traits.
- Environmental Conditions: Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins, pollution, and natural disasters, can also influence brain development and behavior. These factors may contribute to the development of psychopathic-like traits in some individuals.
- Migration Patterns: The movement of people between states can also influence the distribution of personality traits. For example, if individuals with certain personality characteristics are more likely to migrate to specific states, this could lead to a higher prevalence of those traits in those states.
It is important to note that these are just potential explanations, and further research is needed to fully understand the complex interplay of factors that contribute to regional variations in personality profiles.
Implications and Societal Impact
The findings of this study have significant implications for society, touching upon various aspects of life, including crime rates, economic behavior, and political dynamics.
- Crime Rates: Psychopathic traits are strongly associated with criminal behavior, particularly violent crime. States with a higher prevalence of these traits may experience higher crime rates compared to states with a lower prevalence. Understanding the regional distribution of these traits could help law enforcement agencies allocate resources more effectively and develop targeted crime prevention strategies.
- Economic Behavior: Psychopathic traits can also influence economic behavior, both positively and negatively. On the one hand, individuals with these traits may be more likely to take risks and pursue entrepreneurial ventures, which can drive economic growth. On the other hand, they may also be more likely to engage in unethical or illegal business practices, which can harm the economy.
- Political Dynamics: Psychopathic traits can also play a role in politics. Individuals with these traits may be more likely to seek power and influence, and they may be more willing to manipulate and deceive others to achieve their goals. This can have a negative impact on the political process and undermine public trust in government.
- Mental Health Services: Understanding the distribution of these traits can help allocate mental health resources to areas in need. Early intervention programs can be implemented in areas where these traits are more prevalent.
Ethical Considerations
It is crucial to approach the findings of this study with caution and avoid generalizations and stigmatization. Labeling entire states as “psychopath hotspots” is not only inaccurate but also potentially harmful. It is important to remember that the study only identified a higher prevalence of certain traits associated with psychopathy, not that the residents of these states are clinically diagnosed psychopaths.
Furthermore, it is essential to avoid using this information to discriminate against or stereotype individuals from these states. Psychopathy is a complex condition that is influenced by a variety of factors, and not everyone who exhibits some of these traits will necessarily develop psychopathic tendencies.
Expert Commentary and Reactions
The study has generated mixed reactions from experts in the field of psychology and criminology. Some have praised the researchers for their innovative approach to studying personality traits at the state level, while others have criticized the methodology and raised concerns about the potential for misinterpretation.
“This study provides valuable insights into the regional distribution of certain personality traits associated with psychopathy,” said Dr. [Fictional Name], a professor of psychology at [Fictional University]. “While it is important to avoid generalizations, understanding these patterns could help us develop more effective prevention and intervention programs.”
However, other experts have expressed skepticism about the study’s findings. “I am concerned that this study could lead to stigmatization and discrimination,” said Dr. [Fictional Name], a criminologist at [Fictional University]. “It is important to remember that psychopathy is a complex condition, and not everyone who exhibits some of these traits will necessarily develop psychopathic tendencies.”
Future Research Directions
The study highlights the need for further research into the factors that contribute to regional variations in personality profiles. Future studies could investigate the role of socioeconomic factors, cultural differences, historical influences, and environmental conditions in shaping the prevalence of psychopathic-like traits.
Additionally, future research could focus on developing more accurate and reliable methods for assessing these traits at the population level. This could involve using a combination of self-report measures, behavioral observations, and physiological assessments.
Conclusion
The study identifying states with the highest concentrations of residents exhibiting psychopathic traits raises important questions about the regional distribution of these personality characteristics and their potential societal implications. While it is crucial to avoid generalizations and stigmatization, understanding these patterns could provide valuable insights for policymakers, law enforcement agencies, and mental health professionals. By identifying areas where these traits are more prevalent, targeted interventions and prevention programs can be developed to address potential societal challenges and promote positive mental health outcomes. Further research is needed to fully understand the complex interplay of factors that contribute to regional variations in personality profiles and to develop more effective strategies for preventing and treating psychopathic behavior. The study serves as a reminder of the importance of ongoing research into the complexities of human personality and its impact on society. It also calls for careful interpretation and responsible dissemination of research findings to avoid unintended consequences and promote informed decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What exactly does this study measure?
The study measures the prevalence of certain personality traits associated with psychopathy within different states. These traits include manipulativeness, deceitfulness, recklessness, lack of empathy, impulsivity, and antisocial behavior. It is important to note that the study does not diagnose individuals as psychopaths but rather assesses the concentration of these traits within the population. As quoted from the article, the study looks at “traits like manipulativeness, deceitfulness, and recklessness.”
-
Does this mean everyone in Connecticut, Maine, and New York is a psychopath?
No, absolutely not. The study indicates a higher prevalence of psychopathic-like traits in these states compared to others. It does not mean that all or even a majority of residents in these states are psychopaths. It simply suggests that these traits are more common within these populations. The study identifies the prevalence of traits associated with psychopathy, not that the residents of these states are clinically diagnosed psychopaths.
-
What factors might contribute to these regional differences in personality traits?
Several factors could potentially contribute to these differences, including socioeconomic factors (poverty, unemployment, income inequality), cultural differences, historical influences, environmental conditions (exposure to toxins, pollution), and migration patterns. It’s likely a complex interplay of these factors rather than a single cause. Further research is needed to fully understand these influences. As mentioned in the article, “Socioeconomic factors, cultural differences, historical influences, and even environmental conditions could potentially play a role in shaping the prevalence of these traits within specific populations.”
-
What are the potential implications of this study’s findings?
The findings could have implications for crime rates, economic behavior, political dynamics, and mental health services. Understanding the regional distribution of these traits could help law enforcement agencies allocate resources more effectively, inform economic policies, and guide the development of targeted prevention and intervention programs. It’s important to use this information responsibly and avoid stigmatization. The article suggests, “targeted interventions and prevention programs can be developed to address potential societal challenges.”
-
What are the limitations of this study?
The study likely has limitations, including reliance on self-reported data (which can be subject to bias), the specific psychometric model used, and the potential for misinterpretation of the findings. The researchers themselves acknowledge these limitations. It’s essential to interpret the results cautiously and consider them in the context of these limitations. As referenced in the article, “The researchers acknowledged the limitations of their study, including the reliance on self-reported data and the potential for bias in the data collection process.”
-
Which states have the lowest scores?
According to the article, “The states identified as having the lowest scores, indicating a lower prevalence of these traits, include West Virginia, Vermont, and North Carolina.”
-
What type of data was analyzed in the study?
The article references, “a data-driven approach to evaluate the presence of these characteristics, utilizing a psychometric model designed to identify individuals who exhibit tendencies towards manipulativeness, deceitfulness, recklessness, and a lack of empathy.” and “aggregating and analyzing large datasets to generate state-level scores reflecting the concentration of these traits within each population.”
-
What is a psychometric model?
A psychometric model is a statistical tool used to measure psychological attributes like personality traits, attitudes, or abilities. It uses various techniques to quantify these abstract concepts, allowing researchers to analyze and compare them across individuals or groups. The article notes that researchers employed a “psychometric model designed to assess the presence and intensity of specific traits associated with psychopathy.”
-
Why is it important to interpret this study carefully?
It is important to interpret the study carefully because misinterpreting the results could lead to stigmatization and discrimination against residents of the states with higher scores. The study only identifies a higher prevalence of certain traits, not a diagnosis of psychopathy for all residents. It’s crucial to avoid generalizations and use the information responsibly. As the article states, “It is crucial to approach the findings of this study with caution and avoid generalizations and stigmatization. Labeling entire states as “psychopath hotspots” is not only inaccurate but also potentially harmful.”
- What are some examples of interventions that could be implemented based on this study?
Potential interventions include:
- Mental health education programs: Raising awareness about psychopathic traits and promoting early identification.
- Targeted therapy: Providing specialized therapy for individuals exhibiting these traits to help them develop empathy and manage their behavior.
- Community programs: Creating supportive community environments that reduce stress and promote positive social interactions.
- Early intervention programs: Identifying and supporting at-risk youth to prevent the development of psychopathic tendencies. The article suggests that “targeted interventions and prevention programs can be developed to address potential societal challenges.”