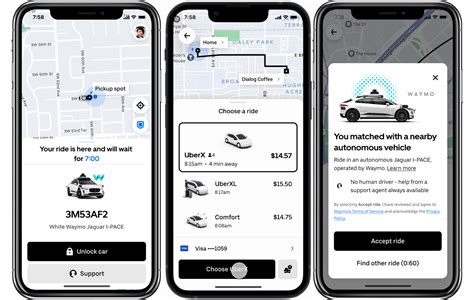
Self-driving car services, once touted as a budget-friendly transportation revolution, are revealing a stark price disparity between competitors Waymo and Uber, with some rides costing significantly more than traditional ride-hailing services and even human-driven taxis. Waymo’s autonomous vehicle (AV) service is turning out to be surprisingly more expensive than Uber’s human-driven ride service, shattering initial expectations of widespread affordability.
A recent analysis of ride costs in areas where both Waymo and Uber operate has exposed considerable differences. While both companies aim to provide convenient transportation, the financial implications for consumers are far from uniform. The data suggests that Waymo, despite its technological advancements and the promise of reduced operational costs through automation, is not necessarily the cheaper option. This discrepancy raises questions about the factors influencing pricing models in the autonomous vehicle industry and the long-term accessibility of self-driving technology for the general public.
The Price Gap in Detail
Several reports and user experiences indicate that Waymo rides can be substantially pricier than comparable Uber rides. One significant factor contributing to this price difference is the operational model each company employs. Waymo, currently operating with a limited fleet and in restricted geographical areas, may have higher per-ride costs due to the capital-intensive nature of deploying and maintaining autonomous vehicles. “It costs a small fortune to run these pilot programs,” noted an expert in autonomous vehicle technology. “The infrastructure, the maintenance, the constant data analysis – it all adds up.”
Uber, on the other hand, benefits from a vast network of human drivers, allowing them to scale their operations more efficiently. While Uber incurs labor costs, the scale of their operations and the flexibility of their driver network provide a cost advantage, at least in the short term. Additionally, Uber’s pricing algorithms are finely tuned based on real-time demand, traffic conditions, and driver availability, allowing them to offer competitive rates, especially during off-peak hours.
The cost comparison isn’t always straightforward. During peak hours or in areas with limited driver availability, Uber’s surge pricing can sometimes exceed Waymo’s standard rates. However, on average, Waymo’s base fares and per-mile charges tend to be higher, making it a less attractive option for budget-conscious riders. The price gap also depends heavily on the specific route, time of day, and demand levels. A short trip during off-peak hours might be cheaper with Uber, while a longer trip during rush hour could potentially be more affordable with Waymo, depending on surge pricing.
Factors Influencing Waymo’s Pricing
Several factors contribute to Waymo’s higher pricing. Firstly, the company is still in the early stages of commercialization. Its operations are primarily focused on select cities, such as Phoenix, Arizona, and San Francisco, California. The limited scale of these operations means that Waymo cannot benefit from the economies of scale that Uber enjoys.
Secondly, the technology itself is expensive. Autonomous vehicles are equipped with a suite of advanced sensors, including LiDAR, radar, and cameras, as well as sophisticated software and processing units. The cost of these components, along with the ongoing maintenance and software updates, contributes to the higher operational costs. “LiDAR alone can cost tens of thousands of dollars per vehicle,” explained a robotics engineer specializing in autonomous navigation. “And that’s just one component. The entire system is incredibly complex and requires constant monitoring and maintenance.”
Thirdly, Waymo invests heavily in safety and redundancy measures. Each autonomous vehicle is equipped with multiple layers of safety systems, including redundant sensors and backup computers. These systems are designed to ensure that the vehicle can continue to operate safely even in the event of a component failure. The cost of these safety measures adds to the overall expense of operating the service.
Fourthly, Waymo’s insurance costs are likely to be higher than Uber’s. While autonomous vehicles are expected to be safer than human-driven vehicles in the long run, insurance companies are still assessing the risks associated with this new technology. As a result, Waymo is likely paying higher premiums to cover potential accidents and liabilities.
The Long-Term Vision
Despite the current price disparity, Waymo and other autonomous vehicle companies remain optimistic about the long-term potential of self-driving technology to reduce transportation costs. The argument is that, as the technology matures and the scale of operations increases, the cost of operating autonomous vehicles will decrease significantly.
One key factor is the elimination of driver labor costs. Human drivers account for a significant portion of the cost of traditional ride-hailing services. By removing the driver from the equation, autonomous vehicle companies can potentially offer lower prices while still maintaining profitability.
Another factor is the potential for increased efficiency. Autonomous vehicles can be programmed to optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and minimize idle time. These efficiencies can translate into lower operating costs and ultimately lower prices for consumers.
Furthermore, as autonomous vehicle technology becomes more widespread, the cost of the underlying components is expected to decrease. Mass production of sensors, software, and processing units will drive down prices, making autonomous vehicles more affordable.
The vision is that autonomous vehicles will eventually become a ubiquitous and affordable mode of transportation, providing a safe, convenient, and cost-effective alternative to traditional ride-hailing services and personal car ownership. “In the long run, autonomous vehicles have the potential to revolutionize transportation,” stated a transportation analyst. “They can reduce congestion, improve safety, and make transportation more accessible to everyone.”
Uber’s Strategy and Challenges
Uber, while facing competition from Waymo and other autonomous vehicle companies, is also investing heavily in self-driving technology. The company recognizes the potential of autonomous vehicles to transform the transportation industry and is working to develop its own self-driving capabilities.
However, Uber’s path to autonomous driving has been fraught with challenges. The company has faced regulatory hurdles, safety concerns, and technical difficulties. In 2018, one of Uber’s autonomous vehicles was involved in a fatal accident in Tempe, Arizona, raising serious questions about the safety of the technology.
Despite these challenges, Uber remains committed to developing self-driving technology. The company believes that autonomous vehicles will play a key role in its future business model. Uber aims to integrate autonomous vehicles into its existing ride-hailing platform, offering customers a choice between human-driven and self-driving vehicles.
Uber’s strategy involves a combination of in-house development and partnerships with other companies. The company has acquired several autonomous vehicle startups and is working with automakers to integrate its self-driving technology into their vehicles.
The Consumer Perspective
For consumers, the price disparity between Waymo and Uber raises important questions about the affordability and accessibility of autonomous vehicle technology. While the long-term vision is for self-driving vehicles to be cheaper than traditional transportation options, the current reality is that they can be more expensive.
This raises concerns about whether autonomous vehicle technology will be accessible to all segments of the population. If self-driving vehicles remain a premium service, they may only be available to wealthier individuals, exacerbating existing inequalities in transportation access.
Furthermore, consumers need to be aware of the factors that influence the pricing of autonomous vehicle services. Demand, time of day, and route distance can all affect the cost of a ride. Consumers should compare prices from different providers before booking a ride to ensure they are getting the best deal.
The price gap between Waymo and Uber also highlights the importance of competition in the autonomous vehicle industry. As more companies enter the market, prices are likely to become more competitive, benefiting consumers.
Regulatory Implications
The deployment of autonomous vehicles is also raising important regulatory questions. Governments around the world are grappling with how to regulate this new technology in a way that promotes safety, innovation, and competition.
One key issue is liability. In the event of an accident involving an autonomous vehicle, it is not always clear who is responsible. Is it the manufacturer of the vehicle, the software developer, or the owner of the vehicle?
Another issue is data privacy. Autonomous vehicles collect vast amounts of data about their surroundings, including information about pedestrians, cyclists, and other vehicles. This data could potentially be used to track individuals’ movements or to discriminate against certain groups.
Governments are also considering regulations related to safety standards, testing requirements, and insurance coverage. The goal is to create a regulatory framework that allows autonomous vehicle technology to develop safely and responsibly.
The Future of Autonomous Vehicle Pricing
The future of autonomous vehicle pricing is uncertain. However, several trends are likely to influence the cost of self-driving services in the coming years.
Firstly, as the technology matures and the scale of operations increases, the cost of operating autonomous vehicles is expected to decrease. This will lead to lower prices for consumers.
Secondly, competition among autonomous vehicle companies will likely drive down prices. As more companies enter the market, they will compete for customers by offering lower prices and better service.
Thirdly, government regulations could affect the pricing of autonomous vehicle services. Regulations related to safety standards, insurance coverage, and data privacy could increase the cost of operating autonomous vehicles, leading to higher prices for consumers.
Fourthly, the development of new business models could also affect pricing. For example, some companies are exploring the possibility of offering autonomous vehicle services on a subscription basis, which could make them more affordable for some consumers.
Conclusion
The price disparity between Waymo and Uber highlights the challenges of commercializing autonomous vehicle technology. While the long-term vision is for self-driving vehicles to be cheaper than traditional transportation options, the current reality is that they can be more expensive.
The factors that influence the pricing of autonomous vehicle services are complex and include the cost of the technology, the scale of operations, safety measures, insurance costs, and regulatory requirements. As the technology matures and the industry evolves, prices are likely to become more competitive, benefiting consumers.
However, it is important to ensure that autonomous vehicle technology is accessible to all segments of the population. Governments and companies should work together to develop policies and business models that promote affordability and equity in transportation access. The self-driving future promises significant changes, but understanding the economic realities alongside the technological advancements is crucial for consumers and policymakers alike. The current price gap serves as a reminder that the path to widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles is not only about technological innovation but also about addressing economic and social considerations.
Expanded Context and Background Information
The development and deployment of autonomous vehicles represent a significant paradigm shift in the transportation sector, promising to reshape urban landscapes, commute patterns, and the very concept of personal mobility. Understanding the historical context, technological underpinnings, and the various players involved is crucial to grasping the current pricing dynamics between companies like Waymo and Uber.
-
The Genesis of Autonomous Vehicle Technology: The pursuit of self-driving vehicles dates back several decades, with early research focusing on basic automation features in automobiles. In the 1980s, projects like the European EUREKA Prometheus Project laid the groundwork for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). However, it was the DARPA Grand Challenges in the early 2000s that truly ignited the modern autonomous vehicle revolution. These challenges incentivized researchers and engineers to develop sophisticated algorithms and sensor systems capable of navigating complex terrains without human intervention.
-
Key Technological Components: Modern autonomous vehicles rely on a suite of advanced technologies, including:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser beams to create a 3D map of the vehicle’s surroundings, providing precise distance measurements and object detection capabilities.
- Radar: Radar sensors use radio waves to detect objects and measure their speed and distance, even in adverse weather conditions.
- Cameras: Cameras provide visual information about the vehicle’s surroundings, allowing the system to identify objects, read traffic signs, and detect lane markings.
- GPS and Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs): These components provide information about the vehicle’s location and orientation, allowing the system to navigate accurately.
- Advanced Algorithms and Software: Sophisticated algorithms process the data from these sensors to create a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle’s environment and make decisions about how to navigate safely.
-
The Players: The autonomous vehicle industry is populated by a diverse range of companies, including technology giants, automakers, startups, and ride-hailing services.
- Waymo: Originally a Google project, Waymo is now a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. and is widely regarded as one of the leaders in autonomous vehicle technology. Waymo has been testing its self-driving vehicles on public roads for over a decade and has accumulated millions of miles of real-world driving data.
- Uber: While primarily known as a ride-hailing service, Uber has also invested heavily in autonomous vehicle technology. The company’s efforts have faced setbacks, but Uber remains committed to developing self-driving capabilities.
- Other Automakers: Major automakers like Tesla, General Motors (Cruise), Ford, and BMW are all developing their own autonomous vehicle technologies. These companies are aiming to integrate self-driving capabilities into their existing vehicle lineups.
- Technology Suppliers: Companies like Intel (Mobileye), NVIDIA, and Qualcomm provide essential hardware and software components for autonomous vehicles.
-
The Regulatory Landscape: The regulation of autonomous vehicles is still evolving. Different countries and states have adopted different approaches to regulating the technology. Some jurisdictions have taken a more permissive approach, allowing companies to test and deploy autonomous vehicles with minimal restrictions. Others have adopted a more cautious approach, requiring extensive testing and safety certifications before allowing autonomous vehicles on public roads. Key regulatory issues include:
- Safety Standards: Establishing safety standards for autonomous vehicles is crucial to ensuring that they operate safely on public roads.
- Liability: Determining liability in the event of an accident involving an autonomous vehicle is a complex legal issue.
- Data Privacy: Protecting the privacy of data collected by autonomous vehicles is an important concern.
- Cybersecurity: Ensuring the cybersecurity of autonomous vehicles is essential to preventing hacking and other malicious attacks.
-
The Economic Implications: The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles could have profound economic implications.
- Job Displacement: The elimination of driver labor could lead to significant job losses in the transportation industry.
- New Business Models: Autonomous vehicles could enable new business models, such as robotaxis and autonomous delivery services.
- Increased Productivity: Autonomous vehicles could increase productivity by allowing people to work or relax while commuting.
- Reduced Congestion: Autonomous vehicles could reduce traffic congestion by optimizing routes and improving traffic flow.
-
The Social Impact: The social impact of autonomous vehicles is also a subject of debate.
- Accessibility: Autonomous vehicles could improve accessibility for people with disabilities or those who are unable to drive.
- Equity: It is important to ensure that autonomous vehicle technology is accessible to all segments of the population, regardless of income or location.
- Urban Planning: Autonomous vehicles could reshape urban landscapes by reducing the need for parking spaces and promoting more efficient land use.
Waymo’s Technological Edge and Operational Strategy
Waymo, widely recognized as a frontrunner in the autonomous vehicle race, has adopted a comprehensive and technologically advanced approach to self-driving. Their strategy hinges on several key elements that contribute to their performance, safety record, and, consequently, their pricing structure.
-
Advanced Sensor Suite: Waymo vehicles are equipped with a multi-layered sensor suite that includes LiDAR, radar, and cameras. The company has invested heavily in developing its own custom LiDAR technology, which provides high-resolution 3D mapping of the vehicle’s surroundings. This proprietary technology, while costly to develop and implement, offers superior object detection and range capabilities compared to off-the-shelf LiDAR systems.
-
Sophisticated Software and Algorithms: Waymo’s self-driving software is built on years of research and development, incorporating advanced algorithms for perception, planning, and control. The software is designed to handle a wide range of driving scenarios, including complex urban environments, inclement weather, and unexpected events.
-
Extensive Testing and Simulation: Waymo has accumulated millions of miles of real-world driving data through extensive testing in various cities. The company also uses advanced simulation tools to test its software in a virtual environment, allowing it to evaluate performance in a wide range of scenarios without risking real-world accidents.
-
Geofencing and Operational Domain: Waymo initially focused its operations in carefully selected and mapped geographical areas (geofencing). This allows them to optimize their software and algorithms for specific environments and to ensure that their vehicles operate safely within those defined boundaries. This limited operational domain, while enhancing safety, also restricts the scale of their operations and contributes to higher per-ride costs.
-
Emphasis on Safety and Redundancy: Waymo prioritizes safety above all else. Its vehicles are equipped with multiple layers of safety systems, including redundant sensors, backup computers, and fail-safe mechanisms. These measures are designed to ensure that the vehicle can continue to operate safely even in the event of a component failure.
Uber’s Approach: Leveraging Existing Infrastructure and Scale
Uber’s approach to autonomous vehicles differs from Waymo’s in several key aspects. Uber is primarily a ride-hailing company with a vast network of human drivers. Its autonomous vehicle strategy is focused on integrating self-driving technology into its existing platform, leveraging its scale and infrastructure to deploy autonomous vehicles more efficiently.
-
Hybrid Approach: Uber aims to offer a hybrid model, combining human-driven and self-driving vehicles on its platform. This allows them to gradually introduce autonomous vehicles into their fleet while still relying on their existing network of drivers.
-
Partnerships and Acquisitions: Uber has pursued a strategy of partnerships and acquisitions to accelerate its autonomous vehicle development. The company has acquired several autonomous vehicle startups and is working with automakers to integrate its self-driving technology into their vehicles.
-
Focus on Affordability: Uber’s primary focus is on affordability. The company aims to offer autonomous vehicle rides at prices that are competitive with traditional ride-hailing services. This requires them to optimize their operations and reduce costs.
-
Data-Driven Optimization: Uber leverages its vast data resources to optimize its pricing algorithms and improve the efficiency of its operations. The company uses data to predict demand, optimize routes, and match riders with drivers.
-
Challenges and Setbacks: Uber’s autonomous vehicle program has faced several challenges and setbacks. A fatal accident involving one of Uber’s self-driving vehicles in 2018 raised serious questions about the safety of the technology and led to a temporary suspension of Uber’s testing program. Despite these challenges, Uber remains committed to developing self-driving technology.
FAQ Section:
Here are 5 frequently asked questions related to the news:
1. Why are Waymo rides currently more expensive than Uber rides, despite the absence of a human driver?
Waymo’s higher prices stem from several factors. Firstly, their operations are still in the early stages of commercialization and confined to select cities, lacking the economies of scale Uber enjoys with its vast network. Secondly, the technology itself is inherently expensive, involving advanced sensors like LiDAR, sophisticated software, and continuous maintenance. Waymo also invests heavily in safety and redundancy measures, including backup systems and extensive testing, further increasing operational costs. Finally, insurance premiums for autonomous vehicles are currently higher due to the nascent nature of the technology and the perceived risks. As the technology matures, production scales, and insurance risks are better understood, Waymo’s prices are expected to become more competitive.
2. How will autonomous vehicles eventually become more affordable than traditional ride-hailing services?
The long-term affordability of autonomous vehicles hinges on the elimination of driver labor costs, which constitute a significant portion of the expense for traditional ride-hailing services. Autonomous vehicles also promise increased efficiency through optimized routing, reduced fuel consumption, and minimal idle time. As the technology matures, the cost of key components like sensors and processing units will decrease due to mass production. Moreover, optimized algorithms and increased fleet utilization will further drive down operational costs, potentially resulting in lower prices for consumers.
3. What are the regulatory hurdles facing the widespread deployment of autonomous vehicles?
The regulatory landscape for autonomous vehicles is still evolving. Key hurdles include establishing clear liability frameworks in case of accidents, addressing data privacy concerns related to the vast amounts of data collected by these vehicles, and ensuring robust cybersecurity measures to prevent hacking and malicious attacks. Governments are also grappling with setting appropriate safety standards, testing requirements, and insurance coverage regulations to ensure safe and responsible deployment of the technology. Varying approaches across different jurisdictions also create complexities for companies operating across state or national borders.
4. How is Uber approaching the development and integration of autonomous vehicle technology?
Uber is pursuing a hybrid approach that combines human-driven and self-driving vehicles on its platform. They aim to gradually integrate autonomous vehicles into their existing network, leveraging their established infrastructure and customer base. Uber relies on a mix of in-house development, partnerships, and acquisitions to advance their self-driving capabilities. Their strategy prioritizes affordability, aiming to offer autonomous rides at competitive prices. Uber also utilizes data-driven optimization to improve routing, pricing, and overall operational efficiency.
5. What are the potential social and economic impacts of the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles?
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles could lead to significant social and economic shifts. Job displacement for professional drivers is a major concern. Conversely, new business models like robotaxis and autonomous delivery services could emerge. Increased productivity is possible as commuters can work or relax during travel. Reduced traffic congestion and optimized urban planning are also potential benefits. Socially, autonomous vehicles could improve accessibility for people with disabilities or those unable to drive. Ensuring equitable access and addressing data privacy concerns are crucial considerations for mitigating potential negative impacts and maximizing the societal benefits of this technology.